WELCOME
Thank you for purchasing Grandstream GSC3510/GSC3505 SIP Intercom speakers. The GSC3505 is a one-way SIP Intercom Speaker and GSC3510 is a two-way full-duplex SIP intercom speaker/microphone, both featuring one 100Mbps Ethernet port with PoE/PoE+, integrated dual-band 2.4G/5G Wi-Fi, integrated Bluetooth, high fidelity 8W speaker and a multi-purpose input port supporting a wide range of peripherals, 3 directional microphones with Multichannel Microphone Array Design (MMAD) available for GSC3510 only. Both GSC3505 and GSC3510 with their Hi-Fi speaker delivers full-band audio, while GSC3510 adds a state-of-art microphone array with pickup distance up to 4.2 meters. The built-in whitelist and blacklist features enable easy filtering of unwanted calls from the Internet. Its modern industrial design and rich features make it ideal for classrooms, hospitals, apartments, dormitories and much more.
PRODUCT OVERVIEW
Feature Highlights
The following table contains the major features of the GSC3510/GSC3505:

GSC3510 GSC3505 |
|
GSC3510/GSC3505 Technical Specifications
The following table resumes all the technical specifications including the protocols / standards supported, voice codecs, telephony features, languages and upgrade/provisioning settings for GSC3510/GSC3505.
Protocols/Standards | SIP RFC3261, TCP/IP/UDP, RTP/RTCP, HTTP/HTTPS, ARP, ICMP, DNS (A record, SRV, NAPTR), DHCP, PPPoE, SSH, TFTP, NTP, STUN, SIMPLE, LLDP-MED, LDAP, TR-069, 802.1x, TLS, SRTP, IPv6, OpenVPN®. |
Network Interfaces | Ethernet RJ45 10/100Mbps ports with integrated PoE/PoE+. |
Bluetooth | Yes, integrated Bluetooth. |
Wi-Fi | Yes, dual-band 2.4 & 5GHz with 802.11 a/b/g/n. |
Alarm Input | 1 Alarm Input Port. |
Voice Codec | G.711µ/a, G.722 (wide-band), G.722.1, G.722.1C, G.726-32, iLBC, Opus, G.729A/B in-band and out-of-band DTMF (In audio, RFC2833, SIP INFO). |
Telephony Features | Hold, transfer, forward (unconditional/no-answer/busy), call park/pickup, downloadable contacts, call record, call log, auto answer, click-to-dial, flexible dial plan. |
HD Audio | Yes, HD speakerphone with support for wideband audio. |
QoS | Layer 2 QoS (802.1Q, 802.1p) and Layer 3 (ToS, DiffServ, MPLS) QoS. |
Security | User and administrator level passwords, MD5 and MD5-sess based authentication, 256-bit AES encrypted configuration file, TLS, SRTP, HTTPS, 802.1x media access control. |
Multi-languages | English, Chinese and Portuguese. |
Upgrade/ Provisioning | Firmware upgrade via TFTP / HTTP / HTTPS or local HTTP upload, mass provisioning using TR-069 or AES encrypted XML configuration file. |
Power and Green Energy Efficiency | Integrated PoE* 802.3af Class 3, PoE+ 802.3at, Class 4. |
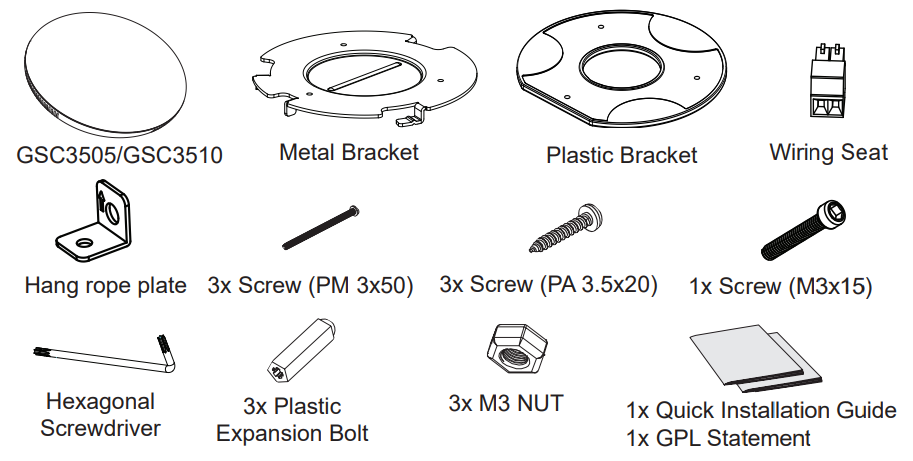
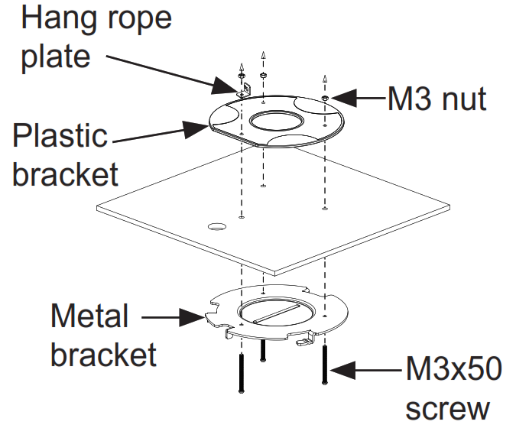
Package Content | GSC3510/GSC3505, Metal Bracket, Plastic Bracket, Wiring Seat, Hang rope plate, 3x Screw (PM 3 x 50), 3x Screw (PA 3.5 x 20), 1 x Screw (M3 x 15), Hexagonal Screwdriver, 3 x Plastic Expansion Bolt, 3 x M3 NUT, Quick Installation Guide, GPL license. |
Physical | Unit Dimensions: 215.32mm (diameter) x 68.7mm (depth)Unit Weight: 0.8kg, Box Weight: 1.39k |
Compliance | FCC: Part 15 (CFR 47) Class B; UL 60950 (power adapter); FCC Part 15C, FCC Part 15E, MPE CE: EN 55032; EN 55024; EN 61000-3-2; EN 61000-3-3; EN 60950-1; EN 301 489-1/17; EN 300 328; EN 301 893; EN 62311; RoHS RCM: AS/NZS CISPR 32/24; AS/NZS 60950.1; AS/NZS 4268 IC: ICES 003, RSS 247, RSP-100, RSS 102 |
GETTING STARTED
This chapter provides basic installation instructions including the list of the packaging contents and also information for obtaining the best performance with the GSC3510/GSC3505.
Equipment Packaging
GSC3510/GSC3505 |
|
GSC3510/GSC3505 Ports
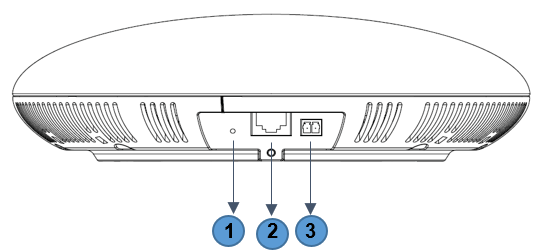
NO. 1 | Name | Description |
RESET | Factory reset button. Press for 10 seconds to reset factory default settings. | |
3 2 | NET/PoE | Ethernet RJ45 port (10/100Mbps) supporting PoE/PoE+. |
2-PIN Port | 2-PIN Multi-Purpose Input Port. |
GSC3510/GSC3505 LED Indicators
The GSC3510/GSC3505 contains 4 types of colored LEDs (Red, Green, White and Blue light) that are used in some specific situations and operations. Please, refer to the following table describing each one of the LED Indicators status:
Color | LED Indicator Status | Description |
Red Light | Fast Flashing (every 1s) | Rebooting/factory resetting |
Slow Flashing (On 1s, Off 2s) | Unhandled event: (Included Missed call(s), new voice mails, new SIP messages). Note: In case the GSC3510/3505 is connected via Bluetooth, Missed Call/Voicemail Red LED will not light and will remain flashing in blue. | |
Solid Red | The contacts/storage space is full | |
Green Light | Fast Flashing (every 1s) | Incoming/outgoing call |
Slow Flashing (On 1s, Off 2s) | Call on hold. | |
Solid Green | During the call. | |
White Light | Fast Flashing (every 1s) | Upgrading the firmware. |
Blue Light | Fast Flashing (every 1s) | Bluetooth pairing. |
Hardware Installation
GSC3510/GSC3505 can be mounted on the wall or ceiling. Please refer to the following steps for the appropriate installation
Wall Mount
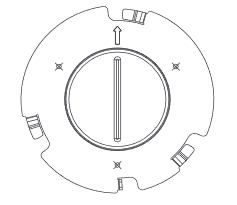
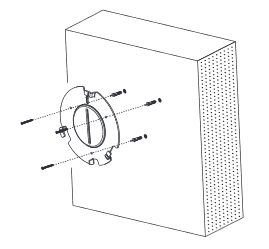
- Locate the equipment holder on the desired position with arrow up. Drill three holes on the wall referring to the positions of holes on the metal bracket.
- Fix the metal bracket on the wall by expansion screws.
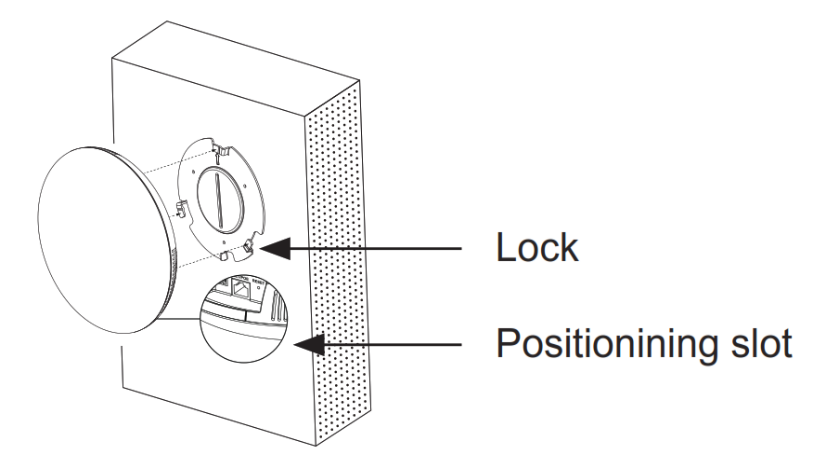
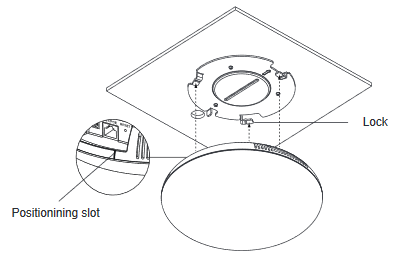
- Align the position line on device’s back cover with the positioning slot.
- Rotate the device clockwise until it is locked on the right position.
Ceiling Mount
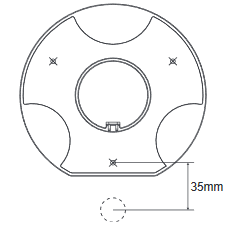
- Put the ceiling mounting (metal bracket) in the ceiling’s center and mark the position of the three screws holes.
- Drill a round hole with a diameter of 18mm for Ethernet cable. The distance between its center and the highlighted hole on the plastic bracket should be 35mm.
- Fix the plastic and metal brackets on the ceiling with flat-head screws and locknuts. Then place and Ethernet cable pass through the 18mm-round hole.
- Align the position line on device’s back cover with the positioning slot.–––
- Rotate the device clockwise until it is locked on the right position.
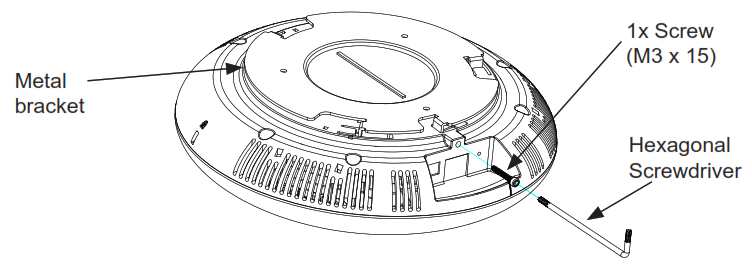
Anti-theft Installation
After the device is assembled with the metal bracket support on the wall or ceiling, use the anti-detachable screw (M3x15) in order to prevent theft.
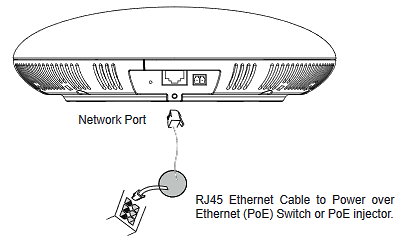
Powering and Connecting GSC3510/GSC3505
The GSC3510/GSC3505 can be powered on using PoE/PoE+ switch or PoE injector using following steps:
- Step 1: Plug a RJ45 Ethernet cable into the network port of the GSC3510/GSC3505.
- Step 2: Plug the other end into the power over Ethernet (PoE) switch or PoE injector.
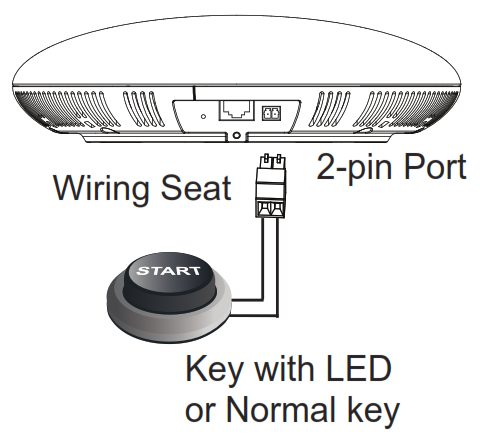
Connecting Wiring Seat
GSC3505/GSC3510 support to connect a “Key & LED” or “Normal Key” to the 2-pin port via Wiring Seat using following steps:
- Step 1: Take the wiring seat from the install kits.
- Step 2: Connect the “Key & LED” or “Normal Key” with the wiring seat (as shown in the figure below)
Access GSC3510/GSC3505 Web GUI
The GSC3510/GSC3505 embedded Web server responds to HTTP/HTTPS GET/POST requests. Embedded HTML pages allow users to configure the application phone through a Web browser such as Microsoft’s IE, Mozilla Firefox, Google Chrome and etc.
Users can use a computer connected to the same network as the GSC3510/GSC3505 to discover and access the GSC3510/GSC3505 Configuration Interface using its MAC Address.
Please, refer to the following steps in order to access the GSC3510/GSC3505 Web GUI:
- Locate the MAC address on the MAC tag of the unit, which is on the underside of the device, or on the package.
- From a computer connected to same network as the GSC3510/GSC3505, type in the following address using the GSC3510/GSC3505’s MAC address on your browser: https://gsc_<mac>.local
Example: if a GSC3510/GSC3505 has the MAC address C0:74:AD:xx:xx:xx, this unit can be accessed by typing https://gsc_c074adxxxxxx.local on the browser.
GSC3510/GSC3505 APPLICATION SCENARIOS
GSC3510/GSC3505 SIP Two-Way/One-Way Intercom System
GSC3510/GSC3505 can be used as an Intercom System using built-in SIP accounts, once the SIP account registered the device can receive paging/intercom calls and it will automatically answer calls coming from whitelisted numbers.
Note: GSC3505 is SIP one-way Intercom, while GSC3510 is two-way Intercom.
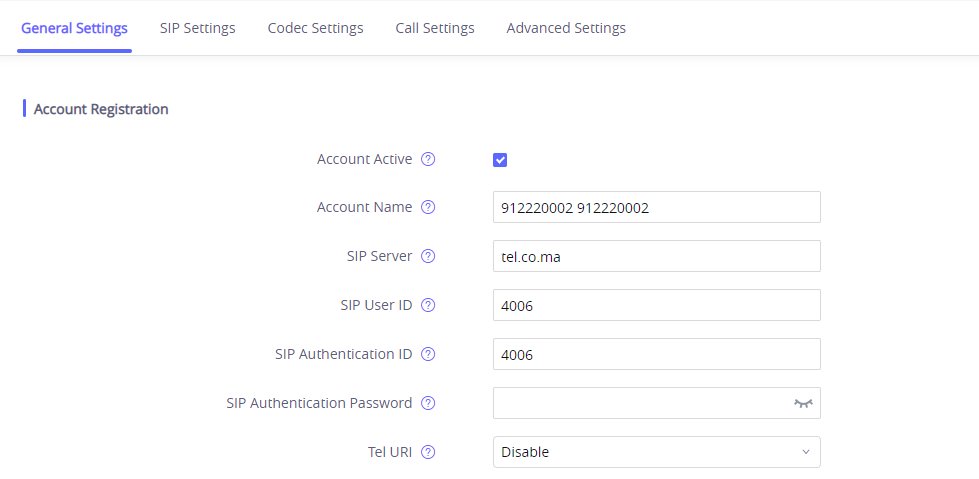
To register a SIP account on the GSC3510/GSC3505 the user needs to go under Account 🡪 Account X 🡪 General Settings, and enter the account information as below, then save and apply the configuration.
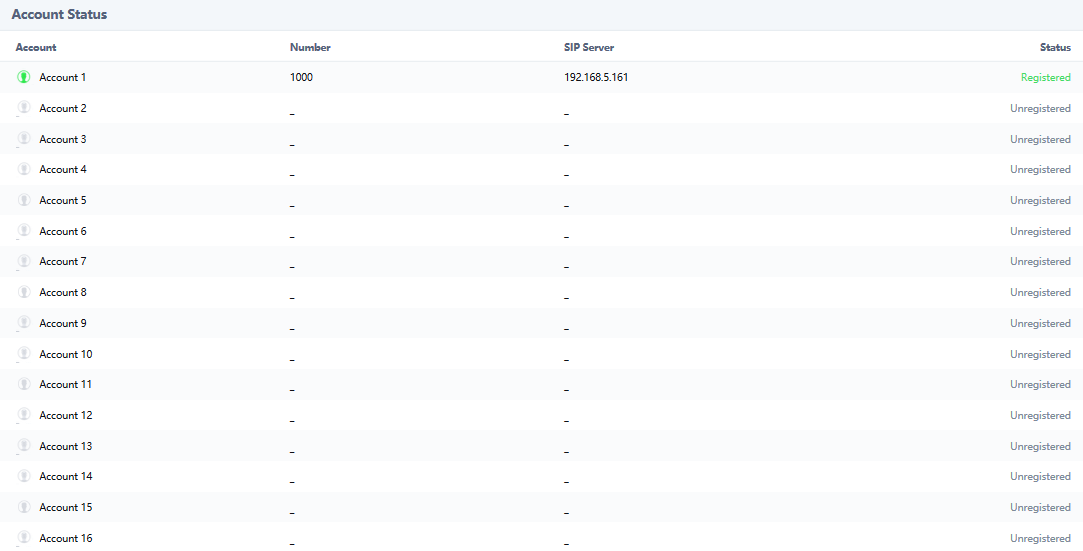
Once the account registered correctly, the GSC3510/GSC3505 will show the account status as “Registered” under Status 🡪 Account Status.
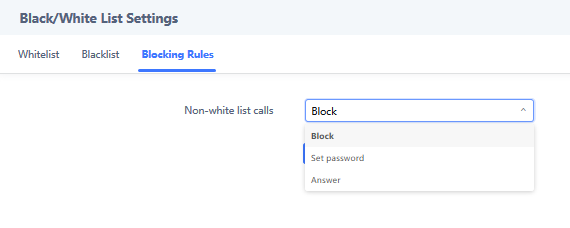
By default, the GSC3510/GSC3505 Blocks non-whitelisted number under Calls 🡪 Black/White List Settings 🡪 Blocking Rules, user needs to either allow Non-White list calls or to set up a Whitelist that contains the number that will be allowed to call the GSC3510/GSC3505.
On the screenshot below, only number 1001 is allowed to call GSC3510/GSC3505:
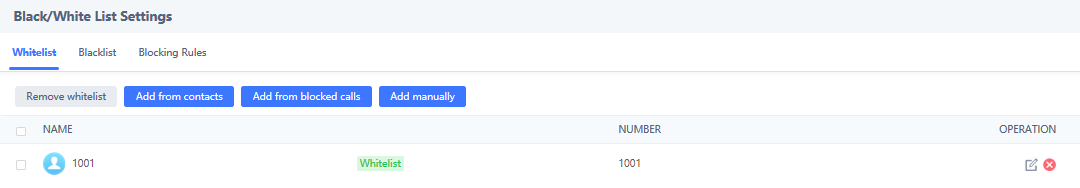
As soon as a SIP call is received by the GSC3510/GSC3505, it first checks if the Caller ID number is allowed on the Whitelist and then answers automatically.
Multicast Paging Application
Multicast paging is an approach to let different SIP users to listen for paging calls from a common multicast IP address. In multicast page call, an audio connection will be set up from sender to receiver, but the receiver will be only able to receive audio, a one-way communication. The 2 entities, Sender/Receiver, must be located on same LAN (same broadcast domain).
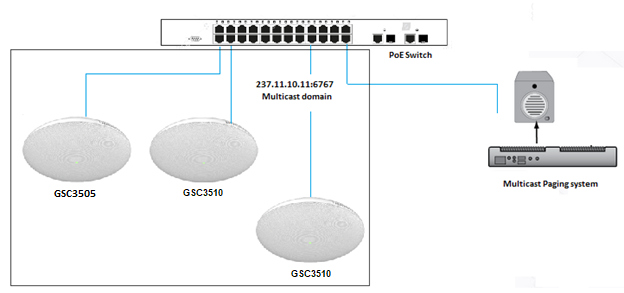
To receive multicast page, GSC3510/GSC3505 must be well configured to listen to the right address and port. The configuration is located under Phone Settings 🡪 Multicast Paging. Up to 10 listening addresses are supported with priority levels from 1 to 10.
Note: Multicast paging configuration requires a reboot to take effect.
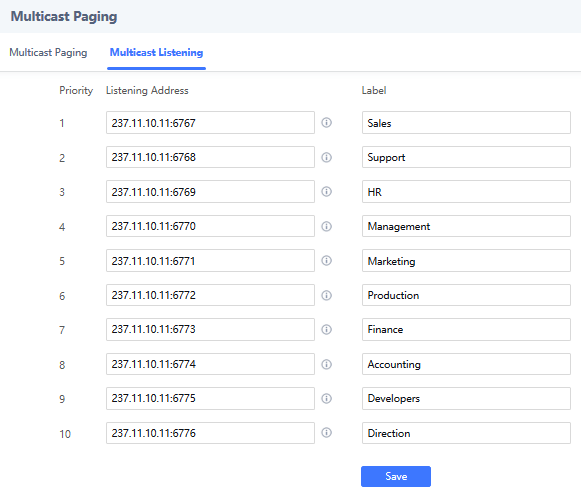
In above screenshot, Listening Address “237.11.10.11:6767” with label “Sales” has the highest priority.
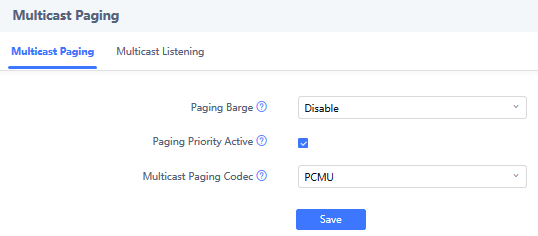
Users can enable “Paging Priority Active” option (under Multicast Paging tab) to accept incoming paging calls during active multicast paging. The paging call with higher priority than active one will be accepted.
In the case of receiving a multicast paging call while on a unicast SIP call, the GSC3510/GSC3505 can choose to either keep the SIP call or to hold this last and allow the multicast call depending on paging call priority.
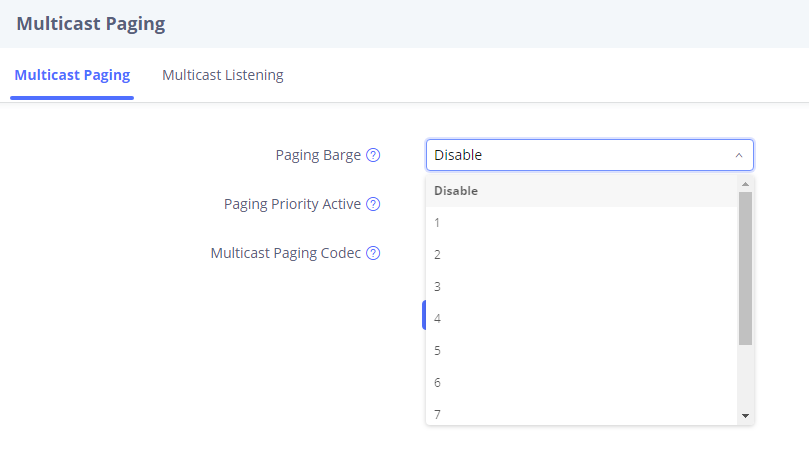
This is can be set using “Paging Barge” option. If the option is set to “Disabled” all incoming multicast paging calls will be dropped while on a SIP call. If the multicast paging call has higher priority than the value set on “Paging Barge”, the SIP call will be put on hold and GSC3510/GSC3505 will the incoming multicast paging.
Bluetooth Speaker
The GSC3510/GSC3505 can be used as a Bluetooth speaker for another device and it needs to be connected via Bluetooth to that device. Users need to turn on GSC3510/GSC3505’s Bluetooth function first. The first time when using a new Bluetooth device with the GSC3510/GSC3505, “pair” the device with GSC3510/GSC3505 so that both devices know how to connect securely to each other.
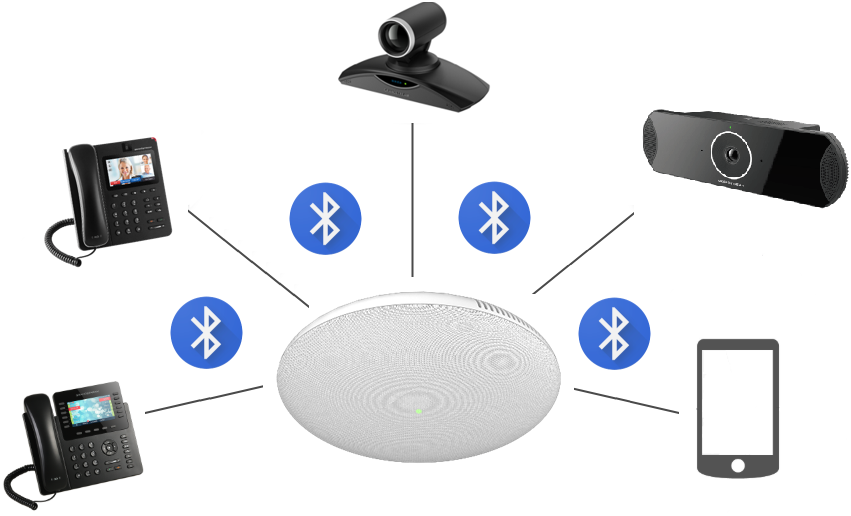
Please, refer to the following steps in order to pair and connect the GSC3510/GSC3505 to the device:
- Go to GSC3510/GSC3505 Web GUI 🡪 Network Settings 🡪Bluetooth Settings.
- Enable “Bluetooth Settings” function, and enable the option “Visible to Nearby Bluetooth Device” in order to make the GSC3510/GSC3505 visible for other devices for 2 minutes (When the 2 minutes are achieved, and you still didn’t connect it, please enable again the option to keep it visible)
- Go to your Device’s Bluetooth settings I order to search for visible devices. The GSC3510/GSC3505 is going to be listed within the visible devices with the “Device Name” configured on the Web GUI.
- Click on the GSC3510/GSC3505 device’s name in order to pair and connect it to the device
2-pin Multi-Purpose Input Applications
GSC3510/GSC3505 supports 2-pin multi-purpose input that can connect a “Key with LED” or “Normal Key”. By configuring the sensor settings users can enable the GSC3510/GSC3505 to play an audio file (.wav/.mp3 format), trigger a SIP call to a pre-configured extension, or to start recording.
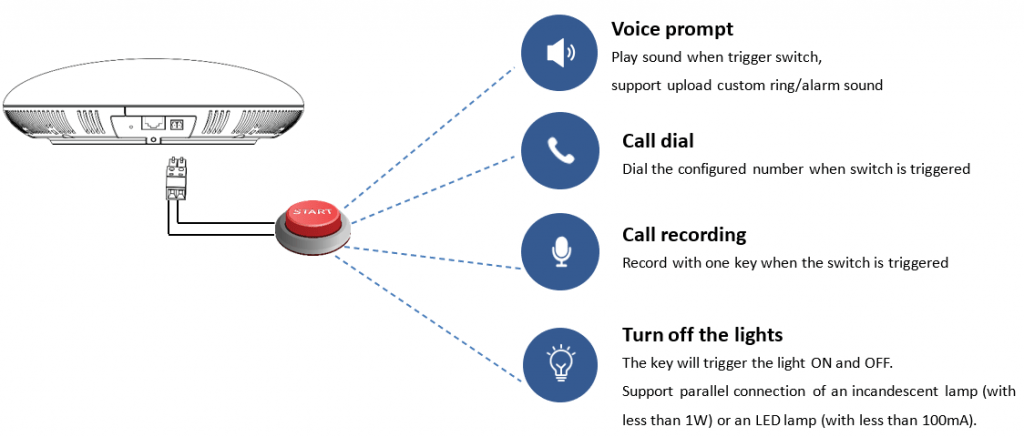
To configure sensor settings, access to web UI 🡪 System Settings 🡪 Sensor Setting.
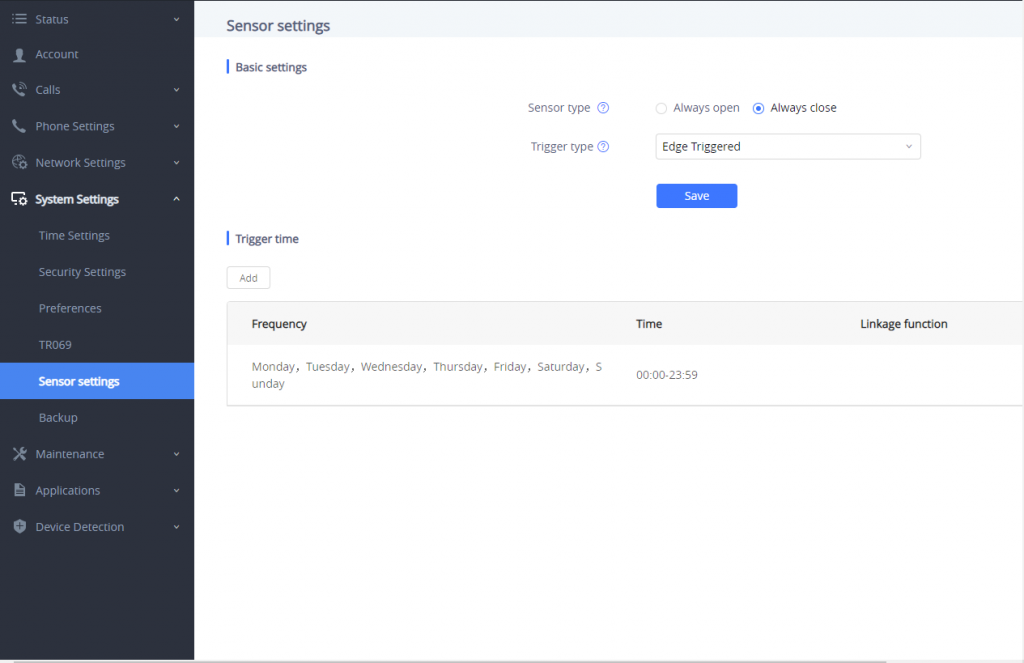
Under Basic Setting section, users can set “Sensor Type” and “Trigger Type”.
Two states are supported by the Input circuit for the “Sensor Type”:
- Normally Open where the contact is disconnected when there is no electricity
- Normally Close where the contact is connected when there is no electricity.
Users could set “Trigger Type” to:
- Edge Triggered: When selected, the notification is triggered only when the level changes (high level to low level, or low level to high level.
- Level Triggered: When selected, only high level (1) will trigger the notification.
Under “Trigger time” section, users can click on “Add” in order to configure different schedules and a trigger profile for each one as shown in the figure below:
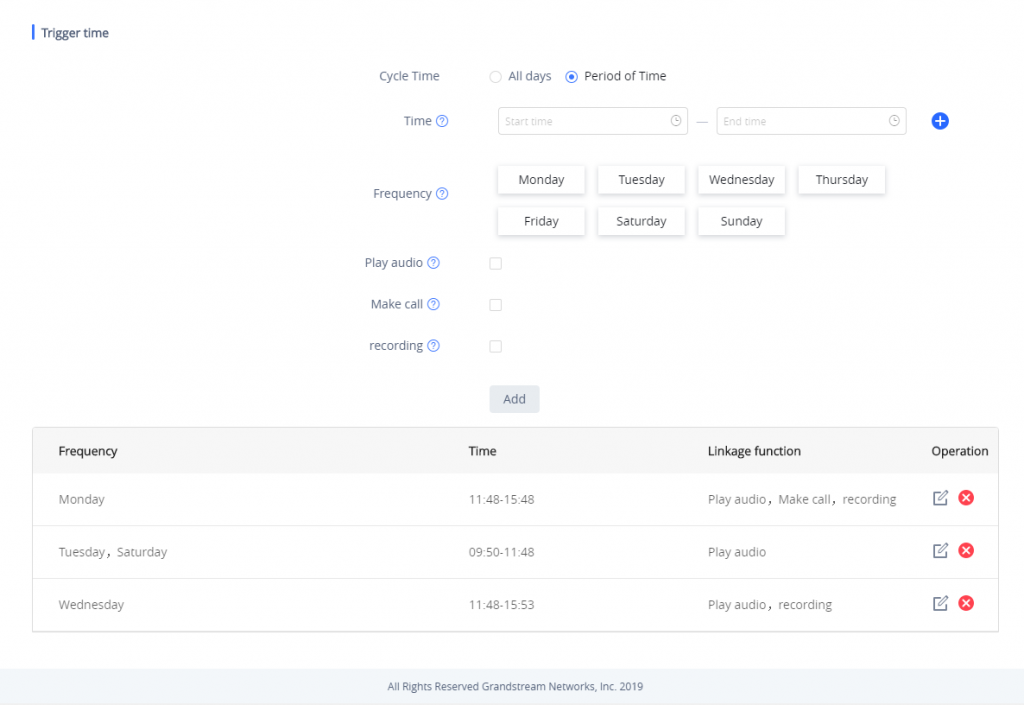
- Cycle Time: The alarm can be configured to be triggered all days of the week, in this case “All days” option needs to be checked. Or to some specific days of the week with Start and End time, in this case “Period of Time” option needs to be checked for users to be able to configure Time and Frequency options.
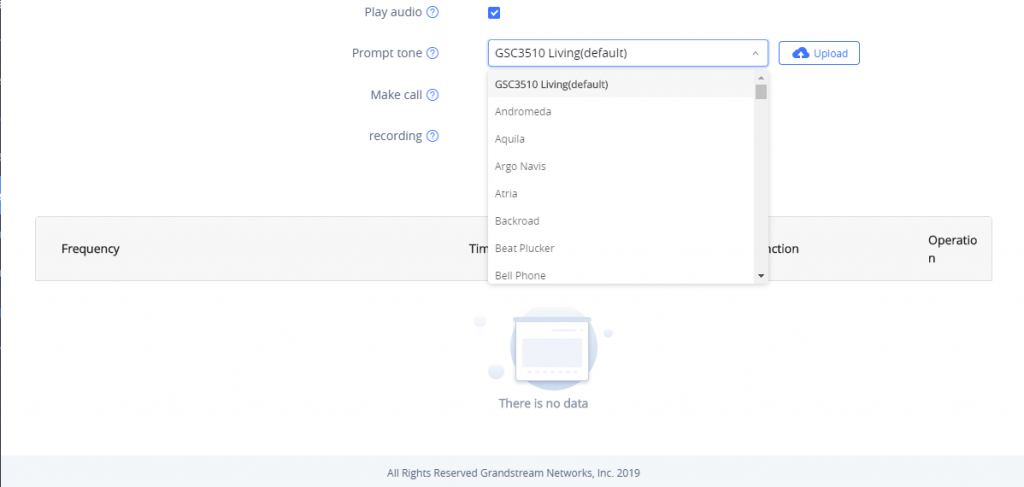
- Play Audio: If checked, GSC3510/GSC3505 will play a sound when the switch is triggered during the schedule. Users can select a “Prompt Tone” from available tones or upload a customized tone.
- Make Call: If checked, GSC3510/GSC3505 will dial out configured numbers on “Dial out extension” fields (up to 2 numbers supported) when the switch is triggered during the schedule.
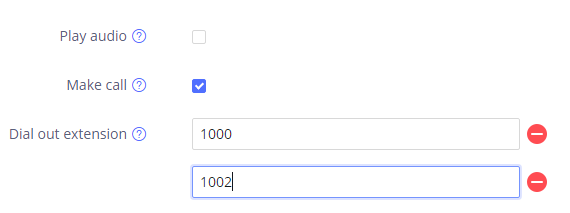
- Recording: If selected, GSC3510/GSC3505 will record audio using built-in microphones. Recorded files can be found under Applications 🡪 Recording
GSC3510/GSC3505 WEB GUI SETTINGS
The GSC3510/GSC3505 embedded Web server responds to HTTP/HTTPS GET/POST requests. Embedded HTML pages allow users to configure the application phone through a Web browser such as Microsoft’s IE, Mozilla ,Firefox, Google Chrome and etc.
Status Page Definitions
Account Status
Account | 16 SIP accounts on the device. |
Number | SIP User ID for the account. |
SIP Server | URL or IP address, and port of the SIP server. |
Status | Registration status for the SIP account. |
Network Status
MAC Address | Global unique ID of device, in HEX format. The MAC address will be used for provisioning and can be found on the label coming with original box and on the label located on the back of the device. |
NAT Type | Type of NAT connection used by the device. |
Address Type | Configured address type: DHCP, Static IP or PPPoE. |
IPv4 Address | IP address of the device. |
Subnet Mask | Subnet mask of the device. |
Default Gateway | Default gateway of the device. |
DNS Server 1 | DNS Server 1 of the device. |
DNS Server 2 | DNS Server 2 of the device. |
IPv6 Address Type | Configured address type: DHCP, Static IP or PPPoE. |
IPv6 Address | IPv6 address of the device. |
IPv6 DNS Server 1 | IPv6 DNS Server 1 of the device. |
IPv6 DNS Server 2 | IPv6 DNS Server 2 of the device. |
System Info
Product Model | Product model of the device: GSC3510/GSC3505. |
Hardware Revision | Hardware version number. |
Part Number | Product part number. |
Serial Number | Product’s serial number. |
System Version | Firmware version ID. This is the main software release version, which is used to identify the software system of the device. |
Recovery Version | Recovery image version. |
Boot Version | Booting code version. |
Kernel Version | The kernel version. |
System Time | Indicates Date and Time. |
System Up Time | System up time since the last reboot. |
Account Page Definitions
GSC3510/GSC3505 has 16 independent SIP accounts. Each SIP account has an individual configuration page.
General Settings
Account Registration | |
Account Active | Indicates whether the account is active. 1st account active by default. |
Configures the name associated with each account. | |
SIP Server | Specifies the URL or IP address, and port of the SIP server. This should be provided by VoIP service provider (ITSP). |
SIP User ID | Configures user account information provided by your VoIP service provider (ITSP). It’s usually in the form of digits similar to phone number or actually a phone number. |
SIP Authentication ID | Configures the SIP service subscriber’s Authenticate ID used for authentication. It can be identical to or different from the SIP User ID. |
SIP Authentication Password | Configures the account password required for the device to authenticate with the ITSP (SIP) server before the account can be registered. After saving, it will appear as hidden for security purpose. |
Display Name | Configures the subscriber’s name (optional) that will be used for Caller ID display. |
Tel URI | Indicates E.164 number in “From” header by adding “User=Phone” parameter or using “Tel:” in SIP packets, if the device has an assigned PSTN Number.
Please consult your carrier before changing this parameter. Default is “Disabled”. |
Network Settings | |
Outbound Proxy | Configures the IP address or the domain name of the primary outbound proxy, media gateway or session border controller. It’s used by the device for firewall or NAT penetration in different network environments. If a symmetric NAT is detected, STUN will not work and only an outbound proxy can provide a solution |
Secondary Outbound Proxy | Sets IP address or domain name of the secondary outbound proxy, media gateway or session border controller. The device will try to connect the Secondary outbound proxy only if the primary outbound proxy fails. |
DNS Mode | Defines which DNS service will be used to lookup IP address for SIP server’s hostname. There are three modes:
To locate the server by DNS SRV set this option to “SRV” or “NATPTR/SRV”. Default setting is “A Record”. |
DNS SRV Fail-over Mode | The option will decide which IP is going to be used in sending subsequent SIP packets (ex: Register refresh requests) after the list of IPs for SIP server host is resolved with DNS SRV.
The device will always prefer to send SIP requests to the available server having the lowest priority, and in case it’s down it contacts the next one, but once the server having lowest priority is UP again, the device will switch over to this one.
On this mode, the device will resolve DNS SRV records and tries to send the request to the server having lowest priority and if it doesn’t respond, it will move on to the next IP until one of the servers responds, once this happen the device will keep contacting this responding IP until DNS timeout (30 minutes) before starting over.
On this mode, the device will send SIP requests to the last responding IP, and it doesn’t failover/switchover to the next one until this responding server is down. |
When this feature is enabled (default), the device will register using the outbound proxy when the SIP server is failed to get the registration. | |
NAT Traversal | Specifies which NAT traversal mechanism will be enabled on the device. It can be selected from the dropdown list:
If the outbound proxy is configured and used, it can be set to “NAT NO”. If set to “STUN” and STUN server is configured, the device will periodically send STUN message to the SUTN server to get the public IP address of its NAT environment and keep the NAT port open. STUN will not work if the NAT is symmetric type. If set to “Keep-alive”, the device will send the STUN packets to maintain the connection that is first established during registration of the device. The “Keep-alive” packets will fool the NAT device into keeping the connection open and this allows the host server to send SIP requests directly to the registered phone. If it needs to use OpenVPN to connect host server, it needs to set it to “VPN”. If the firewall and the SIP device behind the firewall are both able to use UPNP, it can be set to “UPNP”. The both parties will negotiate to use which port to allow SIP through. The default setting is “Keep-alive”. |
Proxy-Require | Adds the Proxy-Required header in the SIP message. It is used to indicate proxy-sensitive features that must be supported by the proxy. Do not configure this parameter unless this feature is supported on the SIP server. |
SIP Settings
SIP Basic Settings | |
SIP Registration | Allows the device to send SIP REGISTER messages to the proxy/server. The default setting is “Yes”. |
Unregister before New Registration | Controls whether to clear SIP user’s information by sending un-register request to the proxy server.
The default setting is “Instance”. |
Register Expiration (m) | Configures the time period (in minutes) in which the device refreshes its registration with the specified registrar. The default setting is 60. The maximum value is 64800 (about 45 days). |
Subscribe Expiration (m) | Specifies the frequency (in minutes) in which the phone refreshes its subscription with the specified register. The maximum value is 64800 (about 45 days). |
Re-register before Expiration (s) | Specifies the time frequency (in seconds) that the device sends re-registration request before the Register Expiration. The default setting is 0. The range is from 0 to 64,800. |
Registration Retry Wait Time (s) | Configures the time period (in seconds) in which the device will retry the registration process in the event that is failed. The default setting is 20. The maximum value is 3600 (1 hour). |
Add Auth Header On RE-REGISTER | Configure if the SIP account needs to add Auth header in RE-REGISTER.
|
Enable SIP OPTIONS Keep Alive | Enables SIP OPTIONS to track account registration status so the device will send periodic OPTIONS message to server to track the connection status with the server. The default setting is “No”. |
SIP OPTIONS Keep Alive Interval (s) | Configures the time interval when the device sends OPTIONS message to SIP server. The default value is 30 seconds, in order to send an OPTIONS message to the server every 30 seconds. The default range is 1-64800. |
SIP OPTIONS Keep Alive Maximum Tries | Configures the maximum times of sending OPTIONS message consistently from the device to server. Phone will keep sending OPTIONS messages until it receives response from SIP server. The default setting is “3”, which means when the device sends OPTIONS message for 3 times, and SIP server does not respond this message, the device will send RE-REGISTER message to register again. The valid range is 3-10. |
Use Privacy Header | Controls whether the Privacy header will present in the SIP INVITE message or not, whether the header contains the caller info. If set to “Yes”, the Privacy Header will always show in INVITE. If set to “No”, the Privacy Header will not show in INVITE. |
Use P-Preferred-Identity Header | Controls whether the P-Preferred-Identity header will present in the SIP INVITE message or not, whether the header contains the caller info. If set to “Yes”, the P-Preferred-Identity Header will always show in INVITE. If set to “No”, the P-Preferred-Identity Header will not show in INVITE. |
SIP Transport | Determines which network protocol will be used to transport the SIP message. It can be selected from TCP/UDP/TLS. Default setting is “UDP”. |
Local SIP Port | Determines the local SIP port used to listen and transmit. The default setting is 5060 for Account 1, 5062 for Account 2, 5064 for Account 3, 5066 for Account 4, 5068 for Account 5, and 5070 for Account 6. The valid range is from 5 to 65535. |
SIP URI Scheme When Using TLS | Defines which SIP header, “sip” or “sips”, will be used if TLS is selected for SIP Transport. The default setting is “sip”. |
Use Actual Ephemeral Port in Contact with TCP/TLS | Determines the port information in the Via header and Contact header of SIP message when the device use TCP or TLS. If set to No, these port numbers will use the permanent listening port on the device. Otherwise, they will use the ephemeral port for the particular connection. The default setting is “No”. |
Support SIP Instance ID | Determines if the device will send SIP Instance ID. The SIP instance ID is used to uniquely identify the device. If set to “Yes”, the SIP Register message Contact header will include +sip.instance tag. Default is “Yes”. |
SIP T1 Timeout | Defines an estimate of the round-trip time of transactions between a client and server. If no response is received in T1, the figure will increase to 2*T1 and then 4*T1. The request re-transmit retries would continue until a maximum amount of time define by T2. The default setting is 0.5 sec. |
SIP T2 Interval | Specifies the maximum retransmit time of any SIP request messages (excluding the SIP INVITE message). The re-transmitting and doubling of T1 continues until it reaches the T2 value. The default setting is 4 sec. |
SIP Timer D Interval | Defines the amount of time that the server transaction can remain when unreliable response (3xx-6xx) received. The valid value is 0-64 seconds. The default value is 0. |
Remove OBP from Route | Configures the device to remove the outbound proxy URI from the Route header. This is used for the SIP Extension to notify the SIP server that the device is behind a NAT/Firewall. If it is set to “Yes”, it will remove the Route header from SIP requests. The default setting is “No”. |
Enable 100rel | Actives PRACK (Provisional Acknowledgment) method. PRACK improves the network reliability by adding an acknowledgement system to the provisional Responses (1xx). It is set to “Yes”, the device will response to the 1xx response from the remote party. Default is “No”. |
Session Timer | |
Enable Session Timer | Allows the device to use the session timer, when set to “Yes”, it will be added in the SIP INVITE message to notify the server. |
Session Expiration (s) | Configures the device’s SIP session timer. It enables SIP sessions to be periodically “refreshed” via a SIP request (UPDATE, or re-INVITE). If there is no refresh via an UPDATE or re-INVITE message, the session will be terminated once the session interval expires. Session Expiration is the time (in seconds) where the session is considered timed out, provided no successful session refresh transaction occurs beforehand. The default setting is 180. The valid range is from 90 to 64800. |
Min-SE (s) | Determines the minimum session expiration timer (in seconds) if the device act as a timer refresher. Default is 90. The valid range is from 90 to 64800. |
UAC Specify Refresher | Sets which party will refresh the active session if the device makes outbound calls. If it is set to “UAC” and the remote party does not support Refresher feature, the device will refresh the active session. If it is set to “UAS”, the remote party will refresh it. If it is set to “Omit”, the header will be omitted so that it can be selected by the negotiation mechanism. The default setting is “Omit”. |
UAS Specify Refresher | Specifies which party will refresh the active session if the device receives inbound calls. If it is set to “UAC”, the remote party will refresh the active session. If it is set to “UAS” and the remote party does not support refresh feature, the device will refresh it. The default setting is “UAC”. |
Caller Request Timer | Sets the caller party to act as refresher by force. If set to “Yes” and both party support session timers, the device will enable the session timer feature when it makes outbound calls. The SIP INVITE will include the content “refresher=uac”. The default setting is “No”. |
Callee Request Timer | Sets the callee party to act as refresher by force. If set to “Yes” and the both parties support session timers, the device will enable the session timer feature when it receives inbound calls. The SIP 200 OK will include the content “refresher=uas”. The default setting is “No”. |
Force Timer | Configures the session timer feature on the device by force.
The default setting is “No”. |
Force INVITE | Sets the SIP message type for refresh the session. If it is set to “Yes”, the Session Timer will be refreshed by using the SIP INVITE message. Otherwise, the device will use the SIP UPDATE or SIP OPTIONS message. Default is “No”. |
Codec Settings
Preferred Vocoder |
|
Preferred Vocoder | Lists the available and enabled Audio codecs for this account. Users can enable the specific audio codecs by moving them to the selected box and set them with a priority order from top to bottom. This configuration will be included with the same preference order in the SIP SDP message. |
Codec Negotiation Priority | Configures the device to use which codec sequence to negotiate as the callee. When set to “Caller”, the device negotiates by SDP codec sequence from received SIP Invite; When set to “Callee”, the device negotiates by audio codec sequence on the device. The default setting is “Callee”. |
Use First Matching Vocoder in 200OK SDP | Configures the device to use the first matching codec in the 200OK message. The default value is 0. |
iLBC Frame Size | Sets the iLBC (Internet Low Bitrate Codec) frame size if ILBC is used. Users can select it from 20ms or 30ms. The default setting is 30ms. |
G726-32 ITU Payload Type | Configures G726-32 payload type for ITU packing mode. Payload 2 is static and payload dynamic is dynamic. The default setting is “2”. |
G726-32 Dynamic Payload Type | Specifies the G726-32 payload type, and the valid range is 96 to 127. The default setting is “126”. |
Opus Payload Type | Defines the desired value (96-127) for the payload type of the Opus codec. The default value is 123. |
DTMF | Specifies the mechanism to transmit DTMF (Dual Tone Multi-Frequency) signals.
There are 3 supported modes: in audio, RFC2833, or SIP INFO.
• In audio, which means DTMF is combined in the audio signal (not very reliable with low-bit-rate codecs);
• RFC2833, which means to specify DTMF with RTP packet. Users could know the packet is DTMF in the RTP header as well as the type of DTMF.
• SIP INFO, which uses SIP INFO to carry DTMF. The defect of this mode is that it’s easily to cause desynchronized of DTMF and media packet if the SIP and RTP messages are required to transmitted respectively.
The default setting is “RFC2833”. |
DTMF Payload Type | Configures the RTP payload type that indicates the transmitted packet contains DTMF digits. Valid range is from 96 to 127. Default value is 101. |
Enable Audio RED with FEC | If set to “Yes”, FEC will be enabled for audio call. The default setting is “No”. |
Audio FEC Payload Type | Configures audio FEC payload type. The valid range is from 96 to 127. The default value is 121. |
Audio RED Payload Type | Configures audio RED payload type. The valid range is from 96 to 127. The default value is 124. |
Silence Suppression | Enables the silence suppression/VAD feature. If it is set to “Yes”, when silence is detected, a small quantity of VAD packets (instead of audio packets) will be sent during the period of no talking. If set to “No”, this feature is disabled. The default setting is “No”. |
Voice Frames Per TX | Configures the number of voice frames transmitted per packet. When configuring this, it should be noted that the “ptime” value for the SDP will change with different configurations here. This value is related to the codec used and the actual frames transmitted during the in-payload call. For end users, it is recommended to use the default setting, as incorrect settings may influence the audio quality.
The default setting is 2. |
RTP Settings |
|
SRTP Mode | Sets if the device will enable the SRTP (Secured RTP) mode. It can be selected from dropdown list:
Disable Enabled but not forced Enabled and forced
SRTP uses encryption and authentication to minimize the risk of denial of service. (DoS). If the server allows to use both RTP and SRTP, it should be configured as “Enabled but not forced”.
The default setting is “Disable”. |
SRTP Key Length | Configures all the AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) key size within SRTP. It can be selected from dropdown list:
AES128&256 bit, AES 128 bit or AES 256 bit
If it is set to “AES 128&256 bit”, the device will provide both AES 128 and 256 cipher suites for SRTP. If set to “AES 128 bit”, it only provides 128-bit cipher suite; if set to “AES 256 bit”, it only provides 256-bit cipher suite. The default setting is “AES128&256 bit”. |
Enable SRTP Key Life Time | Defines the SRTP key life time. When this option is set to be enabled, during the SRTP call, the SRTP key will be valid within 231 SIP packets, and phone will renew the SRTP key after this limitation. The default setting is “Yes”. |
RTCP Destination | Configures a remote server URI where RTCP messages will be sent to during an active call. |
Symmetric RTP | Configures if the device enables the symmetric RTP mechanism. If it is set to “Yes”, the device will use the same socket/port for sending and receiving the RTP messages. The default setting is “No”. |
RTP IP Filter | Receives the RTP packets from the specified IP address and Port by communication protocol. If it is set to “IP Only”, the device only receives the RTP packets from the specified IP address based on the communication protocol; If it is set to “IP and Port”, the device will receive the RTP packets from the specified IP address with the specified port based on the communication protocol. The default setting is “Disable”. |
RTP Timeout (s) | Configures the RTP timeout of the GSC. If the GSC does not receive an RTP packet within the |
Call Settings
Call Features | |
Play Warning Tone for Auto Answer Intercom | When this option is enabled, the device will play a warning tone When auto-answering intercom. The default setting is “yes”. |
Send Anonymous | If set to “Yes”, the “From” header in outgoing INVITE messages will be set to anonymous, essentially blocking the Caller ID to be displayed. |
Intercept Anonymous Calls | If set to “Yes”, anonymous calls will be rejected. |
Call Log | Categorizes the call logs saved for this account. If it is set to “Log All”, all the call logs of this account will be saved. If set to “Log Incoming/Outgoing Calls (Missed Calls Not Record)”, the whole call history will be saved other than missed call. If it is set to “Disable Call All”, none of the call history will be saved. If it is set to “Don’t Prompt Missed Call”, the device will log the missed call histories, but there is no prompt to indicate the missed calls. The default setting is “Log All”. |
Ring Timeout (s) | Defines the expiration timer (in seconds) for the rings with no answer. The default setting is 60. The valid range is from 10 to 300. |
Refer-To Use Target Contact | Sets the device to use the target’s Contact header tag to the Refer-To header in the SIP REFER message during an attended transfer. |
Incoming Call Rules | Allow to set incoming call rules for each account registered. This configuration will over rule the global incoming call rules. If set to “Block”, all greylist calls will be blocked. If set to “Set password”, all greylist calls will need to enter the correct password before they can be answered. If set to “Auto answer”, all greylist calls will be automatically answered. If set to “Ringing”, all greylist calls will continue to ringing. The default ring time is 60s. You can customize the timeout under the Account 🡺 Call setting 🡺 Ring timeout. The default value is “Disable”. |
Auto Answer By CALL-INFO/ALERT-INFO | Configures the Alert-Info content. Only when the info or the parameter in Alert-Info header matches this content would the phone answer the paging call automatically. If set to blank, the paging calls will be ringing according to Incoming Call Rules. This setting only appears if Incoming Call Rules is set to “Ringing…”. |
Dial Plan | |
Dial Plan Prefix | This parameter can be configured to define the prefix added to each dialed number. |
Disable DialPlan | Enables/disables the Dial plan mechanism for different cases. If the specific case is checked, the Dial plan mechanism will be disabled.
|
Dial Plan | Dial Plan Rules: Accepted Digits: 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,0 , *, #, A,a,B,b,C,c,D,d,+ b) xx – only 2-digit numbers c) ^ – exclude d) [3-5] – any digit of 3, 4, or 5 e) [147] – any digit of 1, 4, or 7 f) <2=011> – replace digit 2 with 011 when dialing g) | – the OR operand h) + – add + to the dialing number Example 1: {[369]11 | 1617xxxxxxx} Example 2: {^1900x+ | <=1617>xxxxxxx} Example 3: {1xxx[2-9]xxxxxx | <2=011>x+} Default: Outgoing – { x+ | +x+ | *x+ | *xx*x+ } Example of a simple dial plan used in a Home/Office in the US: {^1900x. | <=1617>[2-9]xxxxxx | 1[2-9]xx[2-9]xxxxxx | 011[2-9]x. | [3469]11 } Explanation of example rule (reading from left to right): ^1900x. – prevents dialing any number started with 1900 |
Advanced Settings
Security Settings | |
Check Domain Certificates | Sets the device to check the domain certificates if TLS/TCP is used for SIP Transport. The default setting is “No”. |
Validate Certification Chain | Configures whether to validate certification chain, when TLS/TCP is configured for SIP Transport. If this is set to “Yes”, phone will validate server against the new certificate list. The default setting is “No”. |
Validate Incoming SIP Messages | Specifies if the device will check the incoming SIP messages caller ID and CSeq headers. If the message does not include the headers, it will be rejected. The default setting is “No”. |
Allow Unsolicited REFER | It is used to configure whether to dial the number carried by Refer-to after receiving SIP REFER request actively. If it is set to “Disabled”, the device will send error warning and stop dialing. If it is set to “Enabled/Force Auth”, the device will dial the number after sending authentication, if the authentication failed, then the dialing will be stopped. If it is set to “Enabled”, the device will dial up all numbers carried by SIP REFER. The default is “Disabled”. |
Only Accept SIP Requests from Known Servers | Answers the SIP request from saved servers when set to “Yes”, only the SIP requests from saved servers will be accepted; and the SIP requests from the unregistered server will be rejected. The default setting is “No”. |
Check SIP User ID for Incoming INVITE | Configures the device to check the SIP User ID in the Request URI of the SIP INVITE message from the remote party. If it doesn’t match the device’s SIP User ID, the call will be rejected. The default setting is “No”. |
Allow SIP Reset | It is used to configure whether to allow SIP Notification message to perform factory reset on the device. The default setting is “No”. |
Authenticate Incoming INVITE | Configures the device to authenticate the SIP INVITE message from the remote party. If set to “Yes”, the device will challenge the incoming INVITE for authentication with SIP 401 Unauthorized response. Default is “No”. |
SIP Realm used for Challenge INVITE & NOTIFY | Configure this item to validate incoming INVITE, but you must enable authenticate incoming INVITE first to make it take effect. You can verify the NOTIFY information for the provision, including check-sync, resync and reboot, but only when SIP NOTIFY authentication enabled first to make it take effect. |
MOH | |
Upload Local MOH Audio File (Music on Hold) | Loads the MOH file to the device. Click on “Browse” button to upload the music file from local PC. The MOH audio file has to be in .wav or .mp3 format. Note: Please be patient while the audio file is being uploaded. It could take more than 3 minutes to finish the uploading especially the file size is large. The button will show as “Processing” during the uploading. Once done, it will show as “Browse” again. Click on “Save” on the bottom of the web page and “Apply” on the top of the web page to save the change. |
Enable Local MOH | Plays local MOH file if the call is being hold by the device. Default is “No”. |
Advanced Features | |
Virtual Account Group | It is used to set to categorize accounts in server mode groups, the accounts in the same group will be combined as one and the account widget will display the Caller ID in the account with lowest ID. The device can answer any incoming calls to each account in groups. If user makes an outbound call, the device will use the lowest ID account by default. If the account fails or SIP INVITE message is timeout, the device will failover to the next account in the group with higher account ID. If all the accounts are not available in the group, the device will traverse all the accounts in the group and notify the users the session is failed. |
Configures phone’s settings to meet different vendors’ server requirements. Users can choose from Standard, NEC, WorldStone, BroadSoft, China Mobile, ZTE IMS, Mobotix or ZTE NGN depending on the server type. |
Calls Page Definition
Call
This page is available for the GSC3510 only.
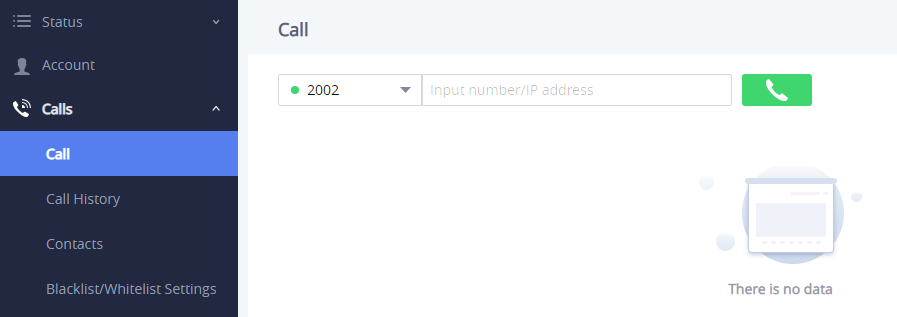
The GSC3510 allows users to manage their calls using the Click to Dial feature which permits to initiate and receive calls using the Web GUI. To use the Click to Dial feature, please refer the following steps:
- Go under the GSC3510 Web GUI 🡪 Calls 🡪 Call.
- Select the account to be used.
-
Type the number / IP Address to call and press Dial button
 as displayed on the following screenshots:
as displayed on the following screenshots:
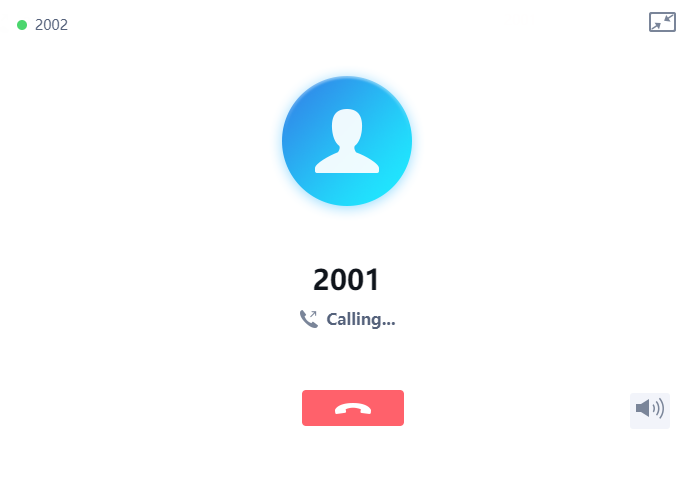
Once the number / IP address is dialed or a Call is received, a window pops up showing the call information and gives the user the ability to do the following operations:
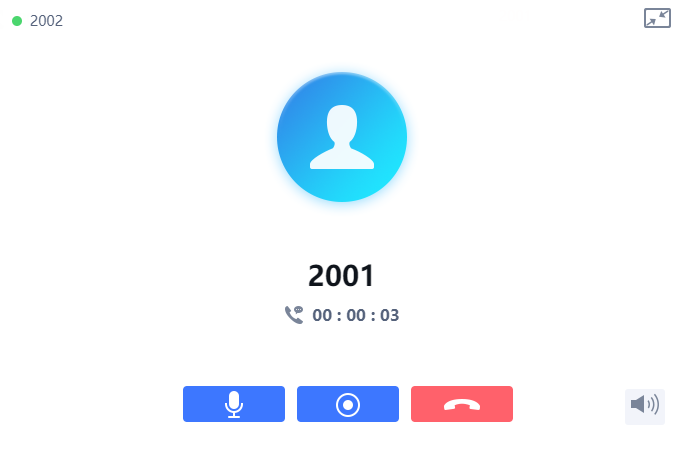
![]() : Reduce the window to a bar at the top of Web GUI interface.
: Reduce the window to a bar at the top of Web GUI interface.
![]() : Adjust the ringing volume.
: Adjust the ringing volume.
![]() : Mute the GSC3510 Mic.
: Mute the GSC3510 Mic.
![]() : Start recording the call.
: Start recording the call.
![]() : End the in-progress call.
: End the in-progress call.
Call History
This page is available for the GSC3510 only.
The GSC3510 Call History is divided into two sections: “All” and “Intercepted Record”:
Call History 🡪 All
This section shows all the calls that have been made or answered. Users can find two types of calls under “Call History → All”:
![]() Outgoing Calls.
Outgoing Calls.
![]() Answered Calls.
Answered Calls.
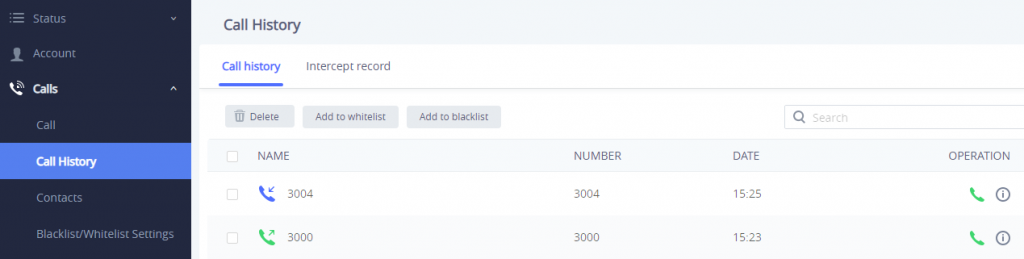
By Tapping on the checkbox to select the call history entries, users can do the following operations:
- Delete Call History: Users need to press the button
 after selecting the call history entries.
after selecting the call history entries.
- Add entries to Whitelist: Users may select the entries to be allowed to call the GSC3510/GSC3505 by clicking on the button
 after selecting the right entries.
after selecting the right entries.
- Add entries to Blacklist: Users can block the calls of some entries by selecting them and pressing the button
 .
.
The following operations can be done as well:
- Make a call to one of the call history entries: Users can directly make a call to a number listed in the call history by clicking directly on the button
 under “OPERATION”.
under “OPERATION”.
- Show calls details: users can show the calls details of a number by clicking on the button
 and a window will pop up to show all the calls sent/received with the selected number.
and a window will pop up to show all the calls sent/received with the selected number.
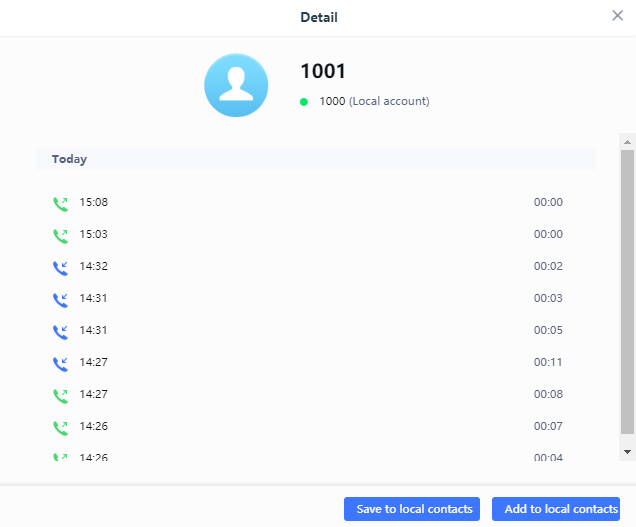
From the Call details window, users can also add the number selected to local contacts by creating a new contact
![]() , or by adding it to an existing contact
, or by adding it to an existing contact
![]() .
.
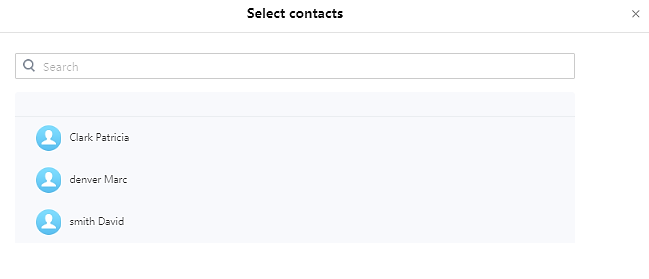
- Add number to an existing contact: Users can click on “Save to local contacts” in order to show a window with all the contacts already registered in the GSC3510/GSC3505 local contacts and to choose one of the contacts to link the selected number with:
- Create a new contact: user can click on “Add to local contacts” in order to show a window where all the information about the contact need to be entered.
Call History 🡪 Intercept Record
This section shows all the calls that have been blocked when received because of not having the permission to make a call to the GSC3510/GSC3505. Users can find only one type of calls under “Call History → Intercept Record”:
![]() Blocked Calls
Blocked Calls
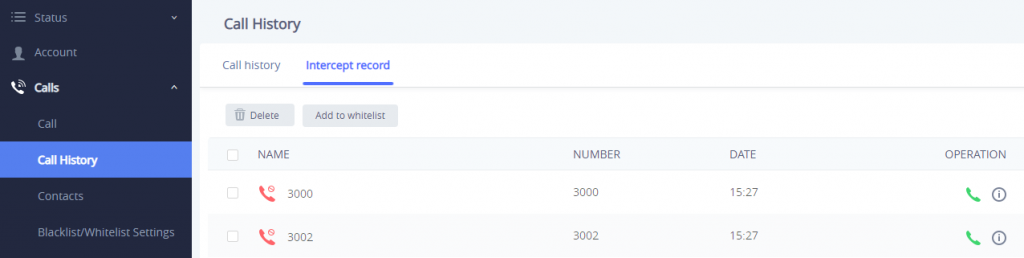
By checking the checkbox to select entries, users can do the following operations:
- Delete Blocked Numbers Call History: Users need to press the button
 after selecting the call history entries.
after selecting the call history entries.
- Add entries to Whitelist: Users may select the blocked entries to give them permission to call the GSC3510/GSC3505 by clicking on the button
 after selecting the right entries.
after selecting the right entries.
The following operations can be done as well:
- Make a call to one of the entries: Users can directly make a call to a number listed in call history → Intercept Record, by clicking directly on the button
 under “OPERATION”.
under “OPERATION”.
- Show calls details: users can show the calls details of a number by clicking on the button
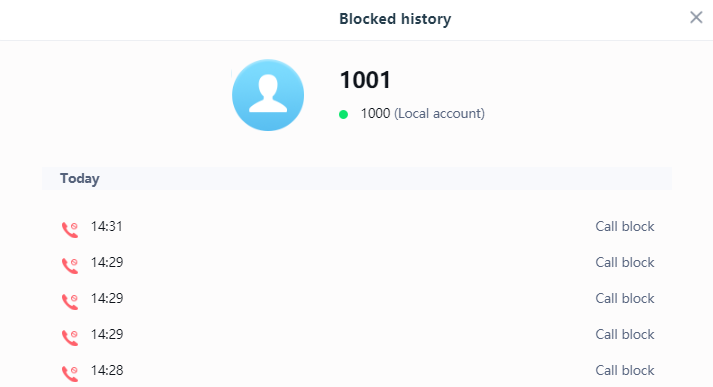
 and a window will pop up to show all the blocked calls received from the selected number.
and a window will pop up to show all the blocked calls received from the selected number.
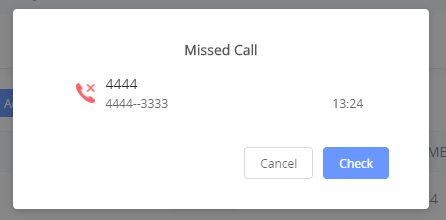
Web GUI Missed Call Notification support
The GSC GUI will display a popup window to notify about missed calls. The figure below contains an example where the Extension 4444 couldn’t reach the GSC at 3333.
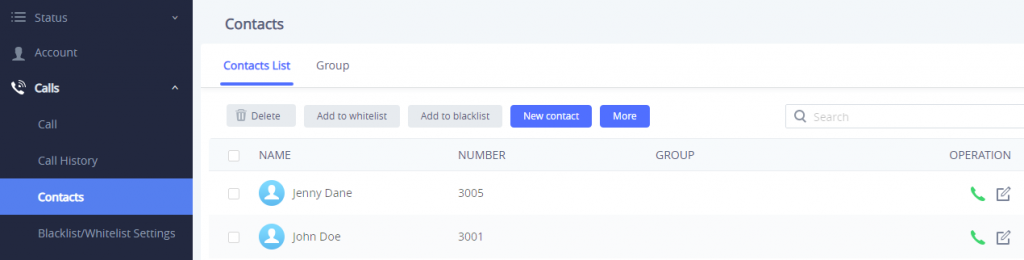
Contacts
Contacts section is divided into two sections: “Contacts List” and “Group”.
Contacts List
-
 Dial Contact (Available for GSC3510 only).
Dial Contact (Available for GSC3510 only).
-
 Edit contact details.
Edit contact details.
-
 : Users can select one or a bench of contacts and click on the “Delete” button order to delete all the selected contacts.
: Users can select one or a bench of contacts and click on the “Delete” button order to delete all the selected contacts.
-
 : Users can select one or bench of contacts and click on the “Add to Whitelist” button in order to directly add the selected contacts to the list of contacts allowed to call the GSC3510/GSC3505.
: Users can select one or bench of contacts and click on the “Add to Whitelist” button in order to directly add the selected contacts to the list of contacts allowed to call the GSC3510/GSC3505.
-
 : Users can select one or bench of contacts and click on the “Add to blacklist” button in order to remove the permission to call the GSC3510/GSC3505 from the selected contacts.
: Users can select one or bench of contacts and click on the “Add to blacklist” button in order to remove the permission to call the GSC3510/GSC3505 from the selected contacts.
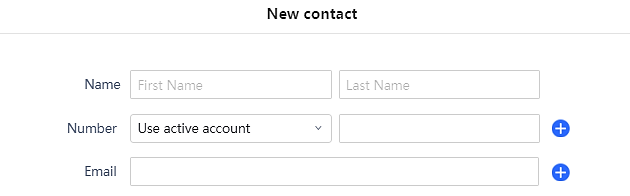
 : Users can create a new contact by clicking on the “New contact” button, then a window pops up (Please, refer to the following figure) in order to enter the new contact’s details.
: Users can create a new contact by clicking on the “New contact” button, then a window pops up (Please, refer to the following figure) in order to enter the new contact’s details.
- : Users need to click on the “More” button for more operations (Import contacts, Export contacts, Download contacts).

Import Contacts | |
Clear The Old List | Determines if the device will delete the previous contacts when a new contact file is imported. If set to “Yes”, the previous contacts will be removed. The default setting is “No”. |
Clear Old History Mode | If set to “Clear all”, the device will delete all previous records before importing the new records. If set to “Keep Local Contacts”, the new-added local new contacts will not be deleted when importing new records. |
Replace Duplicate Items | Configures the device to keep the original contact entries when duplicated contact entries are included in the contact file. If set to “Yes”, the device will replace the original entries to the new one. Otherwise, the device will save both contact entries. The default setting is “No”. |
Replace Duplicate Entries Mode | If set to “Replace by name”, replace the records of the same name automatically when importing new records. If set to “Replace by number”, replace the records of the same number automatically when importing new records. |
File Encoding | Specifies the encoding format for contacts file importing. It can be selected from the dropdown list:
The default setting is UTF-8. |
File Type | Sets the type format for contacts file importing. It can be selected from the dropdown list.
The default setting is “XML”. |
Import Local File | Uploads the contact files from PC to the device. |
Export Contacts | |
File Encoding | Specifies the encoding format for contacts file exporting. It can be selected from the dropdown list:
|
File Type | Sets the type format for contacts file exporting. It can be selected from the dropdown list.
The default setting is “XML”. |
Export | Downloads the contacts file from the device to PC. |
Download Contacts (XML Contacts) | |
Clear The Old List | Sets the device to delete the previous contacts when a new contact file is downloaded. If set to “Yes”, the previous contacts will be removed. The default setting is “No”. |
Clear Old History Mode | If set to “Clear all”, the device will delete all previous records before downloading the new records. If set to “Keep Local Contacts”, the new-added local new contacts will not be deleted when downloading new records. |
Replace Duplicate Items | Keeps the original contact entries when duplicated contact entries are included in the contact file. If set to “Yes”, the device will replace the original entries to the new one. Otherwise, the device will save both contact entries. The default setting is “No”. |
Replace Duplicate Entries Mode | If set to “Replace by name”, replace the records of the same name automatically when downloading new records. If set to “Replace by number”, replace the records of the same number automatically when downloading new records. |
Download Mode | Enables the device to download contacts file and select the server and protocol to download the contacts file. It can be selected from TFTP, HTTP, and HTTPS. The default setting is “OFF”. |
File Encoding | Selects the encoding format for contacts file download. It can be selected from the dropdown list:
The default setting is UTF-8. |
Configures the server URL to download the contacts file. The device will send a request to the server to download the contacts file with filename contacts.xml. | |
HTTP/HTTPS Username | Configures username for HTTP/HTTPS server to download the contacts file. |
HTTP/HTTPS Password | Specifies password for HTTP/HTTPS server to download contacts file. |
Automatic Download Interval | Determines how the device to send the request to the server to download the contacts file. It can be selected from the dropdown list:
|
Download Now | Starts downloading the XML contacts to the device immediately. |
Group
Users could manage the groups of the existing contacts that can be found in “Contacts List”.
Users has the ability to do two operations in this section:
 : Users can select one or a bench of groups and click on the “Delete” button in order to delete all the selected groups.
: Users can select one or a bench of groups and click on the “Delete” button in order to delete all the selected groups.
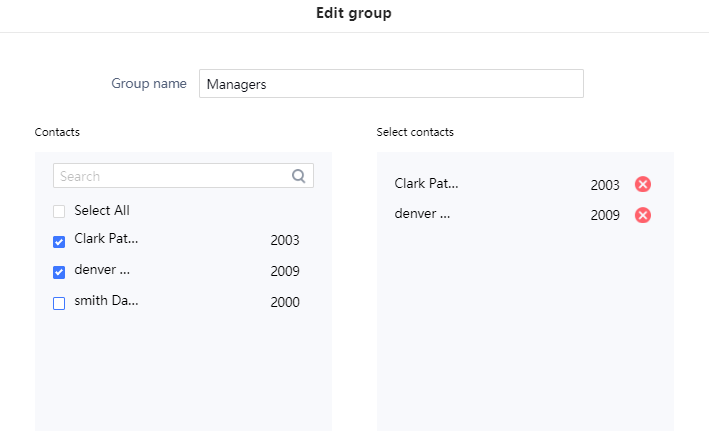
 : Users can create a new group by clicking on the “New group” button, then a window pops up (Please, refer to the following figure) in order to enter the group’s name and specify the contacts that will be included in it.
: Users can create a new group by clicking on the “New group” button, then a window pops up (Please, refer to the following figure) in order to enter the group’s name and specify the contacts that will be included in it.
Black/White List Settings
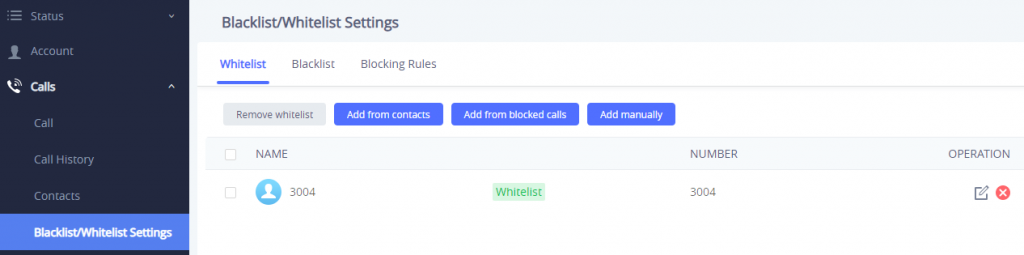
This section is for managing calling permissions to the GSC3510/GSC3505. Users can give or remove the permission to call the GSC3510/GSC3505, this can be managed under the following three subsections:
Whitelist
Users can specify the numbers allowed to call the GSC3510/GSC3505 and every time a number is added it is listed in the below list:
-
 : Users can remove one or a group of numbers from whitelist by clicking in “Remove Whitelist” button.
: Users can remove one or a group of numbers from whitelist by clicking in “Remove Whitelist” button.
Note: Users can also press on to remove one specific contacts from whitelist.
to remove one specific contacts from whitelist.
-
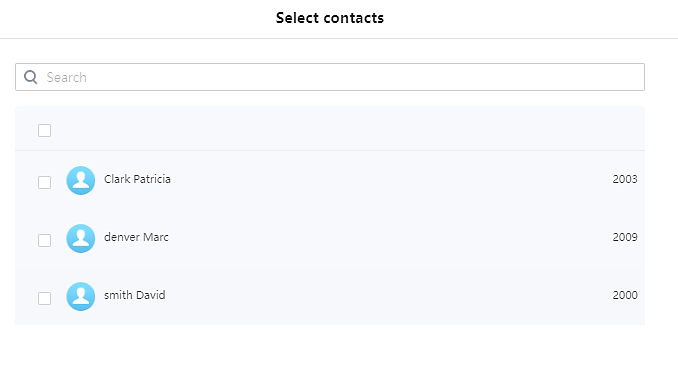
 : Users can add the phonebook contacts to the whitelist by clicking on “Add from contacts” button. A window pops up showing the existing contacts so that users can select the ones wishing to give permission to.
: Users can add the phonebook contacts to the whitelist by clicking on “Add from contacts” button. A window pops up showing the existing contacts so that users can select the ones wishing to give permission to.
-
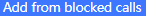 : Users can add the numbers that the GSC3510/GSC3505 is blocking to the Whitelist by clicking on “Add from blocked calls”. A window pops up showing all the blocked numbers.
: Users can add the numbers that the GSC3510/GSC3505 is blocking to the Whitelist by clicking on “Add from blocked calls”. A window pops up showing all the blocked numbers.
-
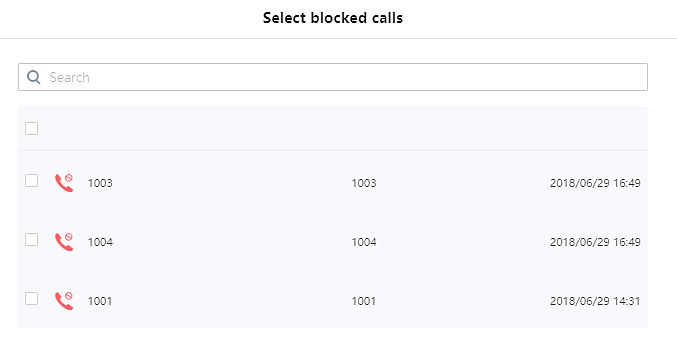
 : Users can add numbers manually to whitelist by clicking on “Add manually” button. A window pops up allowing users to enter the number and its name.
: Users can add numbers manually to whitelist by clicking on “Add manually” button. A window pops up allowing users to enter the number and its name.
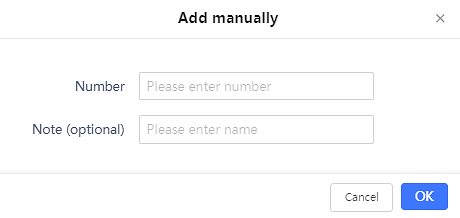
Blacklist
Users can specify the numbers to be blocked by the GSC3510/GSC3505 for incoming calls, and every time a number is added to the blacklist, it is listed in the below list:
-
 : Users can remove one or a group of numbers from blacklist by clicking in “Remove blacklist” button.
: Users can remove one or a group of numbers from blacklist by clicking in “Remove blacklist” button.
Note: Users can also press on to remove one specific contacts from blacklist.
to remove one specific contacts from blacklist.
-
 : Users can add phonebook contacts to the blacklist by clicking on “Add from contacts” button. A window pops up showing the existing contacts so that users may select the ones wishing to give permission to (Please, refer to Figure 23).
: Users can add phonebook contacts to the blacklist by clicking on “Add from contacts” button. A window pops up showing the existing contacts so that users may select the ones wishing to give permission to (Please, refer to Figure 23).
-
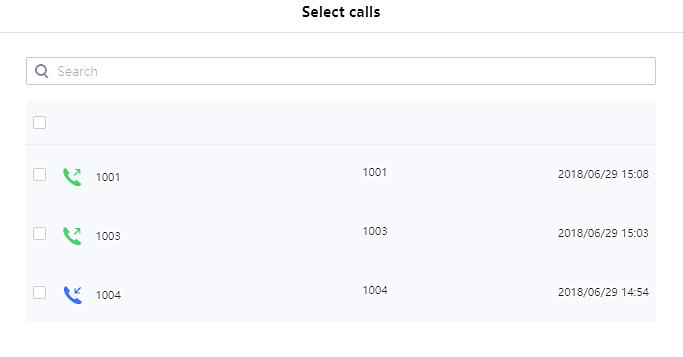
 : Users can add numbers from Call History to the blacklist by clicking on “Add from call history” button. A window pops up showing all the calls listed in the GSC3510/GSC3505 call history.
: Users can add numbers from Call History to the blacklist by clicking on “Add from call history” button. A window pops up showing all the calls listed in the GSC3510/GSC3505 call history.
-
 : Users can add numbers manually to blacklist by clicking on “Add manually” button. A window pops up allowing users to enter the number and its name (Please, refer to Figure 25).
: Users can add numbers manually to blacklist by clicking on “Add manually” button. A window pops up allowing users to enter the number and its name (Please, refer to Figure 25).
Blocking Rules
This sub-section allows the user to define the blocking rules for Non-white list calls. The blocking rules available for the users are:
- Block: Configures the GSC3510/GSC3505 to block all the numbers that are not listed in the Whitelist.
- Answer: Configures the GSC3510/GSC3505 to allow all the calls received from any number but the number listed in the blacklist.
Phone Settings Page Definitions
General Settings
Available for the GSC3510 Only
Basic Settings | |
Local RTP Port | Defines the local RTP port pair used to listen and transmit. The default value is 5004. The valid range is from 1024 to 65400. |
Use Random Port | Forces the device to use random ports for both SIP and RTP messages. This is usually necessary when multiple phones are behind the same full cone NAT. The default setting is “No”. Note: This parameter must be set to “No” for Direct IP Calling to work. |
Keep-alive Interval (s) | Specifies how the device will send a Binding Request packet to the SIP server in order to keep the “ping hole” on the NAT router to open. The default setting is 20 seconds. The valid range is from 10 to 160. |
STUN Server | Configures the URI of STUN (Simple Traversal of UDP for NAT) server. The device will send STUN Binding Request packet to the STUN server to learn the public IP address of its network. Only non-symmetric NAT routers work with STUN. The default setting is “stun.ipvideotalk.com”. |
TURN Server Username | Fill in the username to validate TURN server. |
TURN Server Password | Fill in the password to validate TURN server. |
Use NAT IP | Configures the IP address for the Contact header and Connection Information in the SIP/SDP message. It should ONLY be used if it’s required by your ITSP. By default, the box is blank. |
Call Settings
Enable Call Waiting | Enables call waiting feature. If it is disabled, the GSC3510 will reject the second incoming call during an active session without user’s knowledge. But this missed call record will be saved to remind users. The default setting is checked (enabled). |
Enable Call Waiting Tone | Sets the GSC3510 to play the call waiting tone along with LED indicator if there is another incoming call. If unchecked, only LED will indicate another incoming call. The default setting is checked (enabled). |
Configures the ring time for the unanswered call. The call will be automatically answered after timeout. Default is 5. | |
Configures the timeout for Busy Tone during the call. Default is 30. | |
Auto Mute on Entry | Configures whether to mute the call on entry automatically.
Note: This function only take effect when the device is from the idle status to call status. Users could click the Mute button on call interface to cancel the current mute status. |
Virtual Account Group Avaya Mode | If set to “Yes”, when processing SIP Register 3XX Response, it will parse the address site in 3XX, modify the account server info “SIP Server: port” & “SIP Transaction” in virtual account group and initiate registration again. This feature is designed for the Avaya customers. |
Filter Characters | Sets the characters for filter when dial out numbers. Users could set up multiple characters. For example, if set to “[()-]”, when dial (0571)-8800-8888, the character “()-“ will be automatically filtered and dial 057188008888 directly. |
Escape # as %23 in SIP URI | Determines which characters will be included in the SIP INVITE URI if end users input #. If it is set to “Yes” (Default), the device will replace the # by %23. Otherwise, it will include # in the SIP INVITE message. |
Record Mode | Configures phone recording mode. If set to “Record locally”, then will use the local tape recorder for call recording, and the audio file will be saved in accordance with the tape recorder setup. If set to “Record on PortaOne”, then will send the specified SIP messages to the corresponding server; If set to “Record on UCM”, then will send the recording feature code to the UCM server to request for recording, and the recording function will be executed by the server. |
Environment | Sets operating environment for the device.
The default value is “Large room & used on empty area”. |
Ring Tone
Auto Config CPT by Region | Configures whether to choose Call Progress Tone automatically by region. If set to “Yes”, the device will configure CPT (Call Progress Tone) according to different regions automatically. If set to “No”, you can manual configure CPT parameters. The default setting is “No”. |
Call Progress Tones:
| Configures tone frequencies according to user preference. By default, the tones are set to North American frequencies. Frequencies should be configured with known values to avoid uncomfortable high pitch sounds.
(Frequencies are in Hz and cadence on and off are in 10ms) ON is the period of ringing (“On time” in “ms”) while OFF is the period of silence. In order to set a continuous ring, OFF should be zero. Otherwise it will ring ON ms and a pause of OFF ms and then repeats the pattern. Please refer to the document below to determine your local call progress tones: http://www.itu.int/ITU-T/inr/forms/files/tones-0203.pdf |
Call-Waiting Tone Gain | Adjusts the call waiting tone volume. Users can select “Low”, “Medium” or “High”. The default setting is “Low”. |
Default Ring Cadence | Defines the ring cadence for the device. The default setting is: c=2000/4000. |
Multicast/Group Paging
Multicast Paging | |
Paging Barge | Sets the threshold of paging calls. If the paging call’s priority is higher than the threshold, the existing call will be hold and the paging call will be answered. Otherwise, the existing call does not be affected. If it is set to Disable (Default), any paging call will not be answered. |
Paging Priority Active | Determines if a new paging call whose priority is higher than the existing paging call will be answered. The default is disabled. Check to enable. |
Multicast Listening | |
Priority | Configures the IP address and port number for monitoring multicast paging call. Reboot the device to make changes take effect. |
Listening Address | The valid IP address range is from 224.0.0.0 to 239.255.255.255. |
Label | Label for each listening address corresponding to priority. |
PTT/Group Paging | |
General Settings | |
Listening address | Sets PTT and group paging multicast address. |
Port | Configures port number for group paging address. |
IGMP Keep-alive Interval (s) | Specifies how often the phone reports IGMP when the Group Paging function is turned on. IGMP report helps to keep Group Paging alive in a sleep state. |
Emergency Group Paging Volume | Configures default volume for group paging when emergency channel/group is used. |
PTT Config | |
PTT | Configures to enable or disable PTT. Default is "Disabled" |
Priority Channel | Set priority channel for PTT. PTT received on priority channel will take precedence over active PTT on normal channel. Priorities go from 1 to 25. |
Emergency Channel | Set emergency channel for PTT. Emergency channel has the highest priority. PTT using emergency channel will take precedence over PTT on priority or normal channel. Please note PTT to emergency channel will not be rejected even when device has enabled DND. |
Accept While Busy | Configures whether to accept PTT while device is in active call. If set to "No", device will ignore PTT while in active call. If set to "Yes", while in active PTT talk, device will accept PTT if it has the same priority; If device is in active SIP call, device will accept PTT and put the SIP call on hold. Default is "Disabled" |
Channel | Configures PTT channel. Configures options for the channel such as transport, accept, join PTT and its label. Only available and joined channel will be displayed in PTT channel list. If users need send or receive PTT, "Transport" and "Accept" must be enabled for this channel. |
Paging Config | |
Group Paging | Allows to enable or disable group paging. |
Priority Group | Configures priority paging group. Paging received on priority group will take precedence overactive paging on normal group. |
Emergency Group | Set emergency group for paging. Emergency group has the highest priority. Paging using emergency group will take precedence over paging on priority or normal group. |
Accept While Busy | Configures whether to accept paging while device is in active call. If set to “No”, device will ignore paging while in active call. If set to “Yes”, while in active paging call, the device will accept other paging calls if it has the same priority. If device is in an active SIP call, device will accept paging and hang up the SIP call. |
Group | Configures paging group. Users can configure whether to use the group to accept and join group, and its label. Only available and joined group will be displayed in paging group list. If users need receive paging, “Subscribe” must be enabled for this group. |
Network Settings Page Definitions
Ethernet Settings
Preferred Internet Protocol | If IPv4 is selected, the device will be using IPv4 addressing, otherwise, it will be using IPv6 addressing. Default is Prefer IPv4. |
Different Networks for Data and VoIP Calls | Configures whether to set up different networks for the phone data and the call. If set to “Yes”, you need to configure the data network and VoIP network respectively. Note: Reboot is required to take effect. |
IPv4 | |
IPv4 Address Type | Allows users to configure the appropriate network settings on the device. Users could select “DHCP”, “Static IP” or “PPPoE”.
By default, it is set to “DHCP”. |
DHCP VLAN Override | DHCP Option 132 defines VLAN ID and DHCP Option 133 defines priority tag ID. GSC3510/GSC3505 supports DHCP VLAN override via DHCP Option 132 and DHCP Option 133, or encapsulated DHCP option 132 and DHCP option 133 in DHCP option 43.
By default, it is set to “Encapsulated in DHCP Option 43”: |
Host name (Option 12) | Sets the name of the client in the DHCP request. It is optional but may be required by some Internet Service Providers. Note: You can provide the device MAC in this field by using “$MAC” attribute. |
Vendor Class ID (Option 60) | Configures the vendor class ID header in the DHCP request. Default setting is “Grandstream GSC3510” or “Grandstream GSC3505”. |
Layer 2 QoS 802.1Q/VLAN Tag (Ethernet)
| Assigns the VLAN Tag of the Layer 2 QoS packets for Ethernet. The Default value is 0. Note: When “Different Networks for Data and VoIP Calls” is set to Yes, user needs to set “Layer 2 QoS 802.1Q/VLAN Tag (Ethernet) for Data” and “Layer 2 QoS 802.1Q/VLAN Tag (Ethernet) for VoIP Calls”. |
Layer 2 QoS 802.1p Priority Value (Ethernet)
| Assigns the priority value of the Layer 2 QoS packets for Ethernet. The Default value is 0. Note: When “Different Networks for Data and VoIP Calls” is set to Yes, user needs to set “Layer 2 QoS 802.1p Priority Value (Ethernet) for Data” and “Layer 2 QoS 802.1p Priority Value (Ethernet) for VoIP Calls”. |
IPv6 | |
IPv6 Address | Configures the appropriate network settings on the device. Users could select from “Auto-configured” or “Statically configured”. |
Preferred DNS Server | Configures the Preferred DNS Server. |
DNS Server 1 | Configures the primary DNS IP address. |
DNS Server 2 | Configures the secondary DNS IP address. |
Static IPv6 Address | Enter the static IPv6 address in “Statically configured” IPv6 address type. |
IPv6 Prefix Length | Enter the IPv6 prefix length in “Statically configured” IPv6 address type. Default is 64. |
802.1x Mode | |
802.1x mode | Enables and selects the 802.1x mode for the device. The supported 802.1x modes are: EAP-MD5, EAP-TLS and EAP-PEAP. The default setting is “Disable”. |
802.1x Identity | Enters the identity information for the selected 802.1x mode. (This setting will be displayed only if 802.1 X mode is enabled). |
802.1x Secret | Enters the secret for the 802.1x mode. This option will appear when 802.1x mode is EAP-MD5 or EAP-PEAP. |
CA Certificate | Uploads the CA Certificate file to the device. (This setting will be displayed only if the 802.1 X mode is enabled) |
Client Certificate | Loads the Client Certificate file to the device. (This setting will be displayed only if the 802.1 X TLS mode is enabled) |
Private Key | Loads the private key file to the device. (This setting will be displayed only if the 802.1 X TLS mode is enabled) |
Bluetooth
Bluetooth Settings | Enable or Disable Bluetooth on GSC3510/GSC3505 |
Visible to Nearby Bluetooth Devices | Enable the GSC3510/GSC3505 to be visible via Bluetooth by nearby devices. |
Visibility timeout | Configures visibility timeout to nearby devices before turning back to invisible mode. Default is 2 minutes. |
Set up a 6 digits PIN Code. The PIN is required when pairing other Bluetooth devices. | |
Configures the name that will be shown to other Bluetooth devices. | |
Paired devices | Lists paired devices.
Press
|
Wi-Fi Settings
Connect to Wi-Fi Network
Users can connect wirelessly to a network using Wi-Fi under GSC3510/GSC3505 Web GUI 🡪 Network Settings 🡪 Wi-Fi Settings. In order to connect to a network using Wi-Fi, please, refer to the following steps:
- Go to GSC3510/GSC3505 Web GUI 🡪 Network Settings 🡪 Wi-Fi Settings 🡪 Wi-Fi Basics.
- Enable Wi-Fi Function by turning the option on.
- Click on Scan to show the list of Wi-Fi networks available around the GSC3510/GSC3505
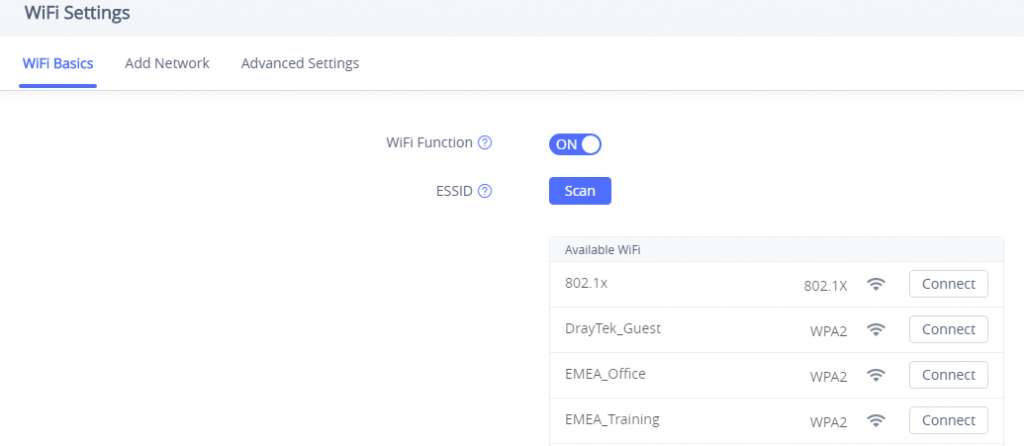
4. Identify the Wi-Fi network’s SSID and click on “Connect”, then enter the correct password information to connect to the selected network:
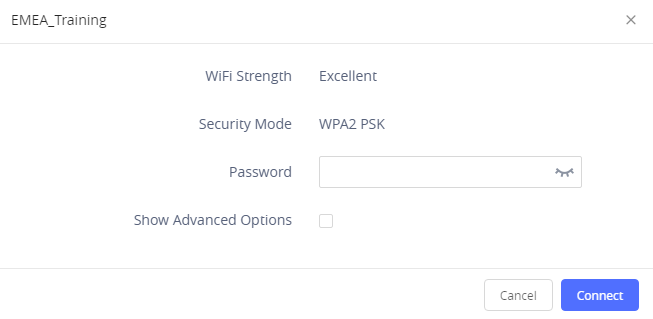
5. Users can check the Wi-Fi parameters and change the setting by checking the “Show advanced options” in the bottom.
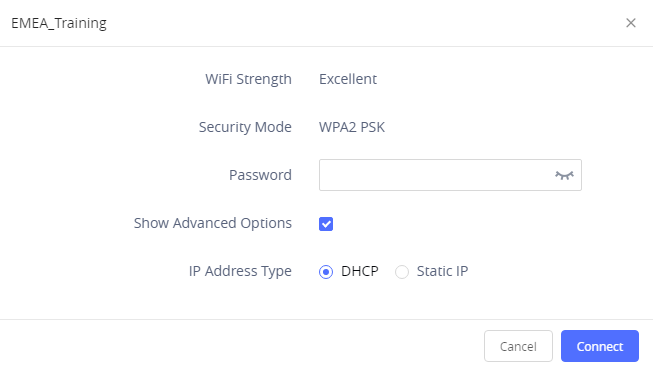
Wi-Fi Settings description
OpenVPN® Settings
OpenVPN ® Settings | |
Enable OpenVPN® | This enables/disables OpenVPN® functionality, and requires the user to have access to an OpenVPN® server. The default setting is No. Note: To use OpenVPN® functionalities, users must enable OpenVPN® and configure all of the settings related to OpenVPN®, including server address, port, OpenVPN® CA, certificate and key. |
Enable OpenVPN® Comp-lzo | Configures enable/disable the LZO compression. When the LZO Compression is enabled on the OpenVPN® server, you must turn on it at the same time. Otherwise, the network will fail to connect. |
OpenVPN® Server Address | The URL/IP address for the OpenVPN® server. |
OpenVPN® Port | The network port for the OpenVPN® server. By default, it is set to 1194. |
OpenVPN® Transport | Determines network protocol used for OpenVPN®: UDP or TCP. |
OpenVPN® CA | OpenVPN® CA file (ca.crt) required by the OpenVPN® server for authentication purposes. Press “Upload” to upload the corresponding file to the device. |
OpenVPN® Client Certificate | OpenVPN® Client certificate file (*.crt) required by the OpenVPN® server for authentication purposes. Press “Upload” to upload the corresponding file to the device. |
OpenVPN® Client Key | The OpenVPN® Client key (*.key) required by the OpenVPN® server for authentication purposes. Press “Upload” to upload the corresponding file to the device. |
OpenVPN® Cipher Method | The cipher method of OpenVPN®, must be the same cipher method used by the OpenVPN® server. Available methods are:
Default is “Blowfish” |
OpenVPN® Username | OpenVPN® authentication username (optional). |
OpenVPN® Password | OpenVPN® authentication password (optional). |
Advanced Network Settings
Advanced Network Settings | |
Configures the refresh time (in minutes) for DNS query. If set to “0”, the phone will use the DNS query TTL from DNS server response. | |
Configures the duration (in minutes) of previous DNS cache when DNS query fails. If set to “0”, the feature will be disabled. Note: Only valid for SIP registration. | |
IPv4 Preferred DNS 1 Server | Sets the preferred DNS server 1 for the user. |
IPv4 Preferred DNS 2 Server | Sets the preferred DNS server 2 for the user. |
Enable LLDP | Enables the LLDP (Link Layer Discovery Protocol) feature on the device. If it is set to “Yes”, the device will broadcast LLDP PDU to advertise its identity and capabilities and receive same from a physical adjacent layer 2 peer. The default setting is “Yes”. |
LLDP TX Interval (s) | Configures the interval the device sends LLLD-MED packet. The default setting is 30s. Note: Reboot the device to make changes take effect. |
Enable CDP | Configures whether to enable CDP to receive and/or transmit information from/to CDP-enabled devices. The default setting is “No”. |
Layer 3 QoS for SIP | Defines the Layer 3 packet’s QoS parameter for SIP messages in decimal pattern. This value is used for IP Precedence, Diff-Serv or MPLS. Default setting is 48 which is equivalent to the DSCP name constant CS6. |
Layer 3 QoS for Audio | Defines the Layer 3 packet’s QoS parameter for RTP messages in decimal pattern. This value is used for IP Precedence, Diff-Serv or MPLS. Default setting is 48 which is equivalent to the DSCP name constant CS6. |
HTTP/HTTPS User-Agent | Sets the user-agent for contacts. Note: Reboot the device to make changes take effect. |
SIP User-Agent | Sets the user-agent for SIP. Default is:
|
Proxy | |
HTTP/HTTPS Proxy Hostname | Specifies the HTTP/HTTPS proxy hostname for the device to send packets to. The proxy server will act as an intermediary to route the packets to the destination. |
HTTP/HTTPS Proxy Port | Specifies the HTTP/HTTPS proxy port for the device to send packets to. The proxy server will act as an intermediary to route the packets to the destination. |
Bypass Proxy For | Defines the destination IP address where no proxy server is needed. The device will not use a proxy server when sending packets to the specified destination IP address. |
System Settings Page Definitions
Time Settings
Time Settings | |
Assign NTP Server Address | Defines the URL or IP address of the NTP server. The phone may obtain the current date and time information from the server. The default setting is “pool.ntp.org”. |
DHCP Option 42 Override NTP Server | Obtains NTP server address from a DHCP server using DHCP Option 42; it will override configured NTP Server. If set to “No”, the phone will use configured NTP server to synchronize time and date even if a NTP server is provided by DHCP server. The default setting is “Yes”. Note: Changes in this setting need reboot to take effect. |
DHCP Option 2 to Override Time Zone Settings | Obtains time zone setting (offset) from a DHCP server using DHCP Option 2; it will override selected time zone. If set to “No”, the phone will use selected time zone even if provided by DHCP server. The default setting is Yes. Note: Changes in this setting need reboot to take effect. |
Time Zone | Specifies the local time zone for the phone. It covers the global time zones and user can selected the specific one from the drop-down list. |
Time Display Format | Specifies which format will be used to display the time. It can be selected from 12-hour and 24-hour format. |
Date Display Format | Determines which format will be used to display the date. It can be selected from the drop-down list.
The default setting is MM/DD/YYYY |
Security Settings
Web/SSH Access | |
Enable SSH | Enables/disables SSH access to the device. The default setting is “Yes”. |
Allow web page access | Allow web page access, If set to “NO”, the Web UI will not be accessible. Please turn it on carefully. The setting requires reboot to take effect. Enabled by Default. |
SSH Port | Customizes the SSH port. By default, SSH uses port 22. |
Access Method | Determines which protocol will be used to access the device ‘s Web GUI. It can be selected from HTTP and HTTPS. The default setting is HTTP. |
Port | Specifies which port to use to access the Web UI. By default, if HTTP, the port number will be 80; if HTTPS is selected, the port number will be 443. |
Enable User Web Access | The Administrator can disable or enable user web access through this option. |
User Login Timeout | Configures login timeout (in minutes) for the user. If there is no activity within the specified time, the user will be logged out, and the Web UI will go to the login page automatically. |
User Info Management | |
Current Admin Password | Enter current logged-in user’s password. This field is case-sensitive. The default password can be found on the sticker on the back of the device. Note: Admin username is “admin”. |
New Admin Password | Allows the user to change the admin password. The password field is purposely blank after clicking the “Save” button for security purpose. This field is case sensitive with a maximum length of 32 characters. |
Confirm Admin Password | Enter the new Admin password again to confirm. |
New User Password | Allows the administrator to set the password for user-level web GUI access. This field is case sensitive with a maximum length of 32 characters. The default password is “123”.
|
Confirm New User Password | Enter the new User password again to confirm. |
Encryption Settings | |
TLS | |
Minimum TLS Version | Specifies the minimum TLS version allowed for the connection. |
Maximum TLS Version | Specifies the maximum TLS version allowed for the connection. Default is 99. |
Enable Weak TLS Cipher Suites | Configures the function for weak TLS cipher suites. If set to "Enable Weak TLS Cipher Suites", the data will be encrypted by weak TLS cipher suites. If set to "Disable Symmetric Encryption RC4/DES/3DES", weak cipher DES/3DES and RC4 will be disabled. |
SIP TLS | |
SIP TLS Certificate | Defines the SSL certificate used for SIP over TLS. |
SIP TLS Private Key | Defines the SSL Private key used for SIP over TLS. |
SIP TLS Private Key Password | Defines the SSL Private key password used for SIP over TLS. |
Certificate Management | |
CA Certificate | |
Import Trusted CA Certificates | Allows to upload the CA Certificate file to phone. Note: Reboot is required to take effect. |
Trusted CA Certificates | Lists trusted CA certificates previously uploaded. Administrator can delete a certificate from here. |
User Certificate | |
Add User Certificate | Allows to upload & Install User Certificate file to phone. |
User Certificates | Lists Users Certificates previously uploaded. Administrator can delete a certificate from here. |
Custom Certificate | |
Import Custom Certificate | Allows to upload & Install Custom Certificate file to device. |
Custom Certificate | Lists Custom Certificates previously uploaded. Administrator can delete a certificate from here. |
Preferences
LED Management | |
Disable Missed Call Indicator | If set to “Yes”, the LED indicator will not light up when there is missed call on the device. |
Disable Contact Full Indicator | If set to “Yes”, the LED indicator will light up when the contact storage or message storage is full. |
Brightness Control | |
Red Light | Control the intensity of the Red Color in the LED |
Green Light | Control the intensity of the Green Color in the LED |
Blue Light | Control the intensity of the Blue Color in the LED |
Volume Settings | |
Call Volume | Sets the volume of calls. |
Ringtone volume | Sets the volume of ringtones. |
Media volume | Sets the volume of media. |
TR-069
Enable TR-069 | Sets the device to enable the “CPE WAN Management Protocol” (TR-069). The default setting is “No”. Note: Reboot the device to make changes take effect. |
ACS URL | Specifies URL of TR-069 ACS (e.g, http://acs.test.com), or IP address. |
ACS Username | Enters username to authenticate to ACS. |
ACS Password | Enters password to authenticate to ACS. |
Periodic Inform Enable | Sends periodic inform packets to ACS. Default is “No”. |
Periodic Inform Interval (s) | Configures to sends periodic “Inform” packets to ACS based on specified interval. The default setting is 86400. |
Connection Request Username | Enters username for the ACS to connect to the device. |
Connection Request Password | Enters password for the ACS to connect to the device. |
Connection Request Port | Enters the port for the ACS to connect to the device. |
CPE Cert File | Uploads Cert File for the device to connect to the ACS via SSL. |
CPE Cert Key | Uploads Cert Key for the device to connect to the ACS via SSL. |
Sensor Settings
Basic Settings | |
Basic Settings | |
Sensor Type | Set the initial state of the sensor, when the selection is normally open, the contact is disconnected when static; When the selection is normally closed, the contact is connected when static. The normally open will be connected when the electrical action is on the switch, and the normally closed will disconnected. The default is normally open. |
Trigger Type | Set the type of the trigger mode, and when the selection is level triggered, only high level (1) or low level (0) will trigger the notification. When the edge trigger is selected, the notification is triggered only when the level changes (high level to low level, or low level to high level). The default is level trigger. |
Trigger time | |
Cycle Time | The alarm can be configured to be triggered all days of the week, in this case “All days” option needs to be checked. Or to some specific schedule, in this case “Period of Time” option needs to be checked for users to be able to configure Time and Frequency options below. |
Time | Set the activation time, up to 3 times. When the activation time is not set, the default time is full day. |
Frequency | Set the activation frequency from Monday to Sunday, which can be selected from the whole week. The default value is not selected. |
Play Audio | Play a sound when the switch is triggered during the scheduled time. |
Prompt Tone | When the “voice prompt” is selected, you can upload the customized audio by clicking on “Upload” and choose the file. |
Make Call | Dial the number when the sensor is activated. |
Dial out extension | Enter the number you need to dial and click the “add” button to set two numbers at the same time. |
Hang up | Hang up calls when the sensor is triggered, such as SIP call, multicast, etc. When checked at the same time as Make Call, if there is currently a call, the first trigger will hang up the call, and the second trigger will dial. |
Backup
GSC3510/GSC3505 Backup page is used to back up data or import backup files to restore data. Users can start the Backup by clicking on “Start Backup”.
The following data on the GSC3510/GSC3505 can be backed up and restored to the device again using the built-in Backup application: Contacts, Call history, Configuration information.
Once the wanted Backup contents are checked, users can generate the backup by clicking on “Backup”.
The backup will be shown with all the needed information (Back Content, Backup Time and Backup Size).
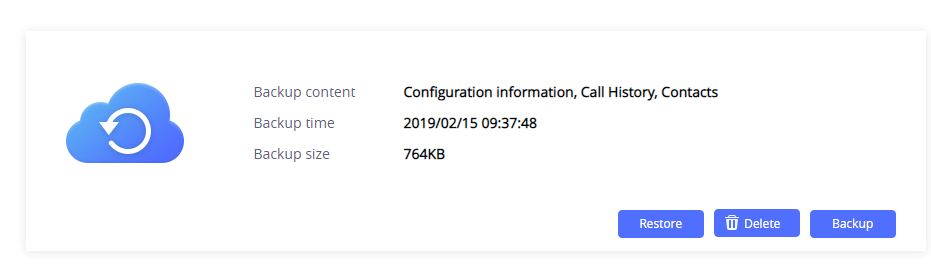
By generating the Backup, users can do the following operations:
-
 : Users can bring back to the GSC3510/GSC3505 all the backup contents selected during Back generating operation by clicking on “Restore”.
: Users can bring back to the GSC3510/GSC3505 all the backup contents selected during Back generating operation by clicking on “Restore”.
-
 : Users can delete the generated Backup by clicking on “Delete”.
: Users can delete the generated Backup by clicking on “Delete”.
-
 : Users needs to click on “Backup” to generate a new backup and replace the existing one.
: Users needs to click on “Backup” to generate a new backup and replace the existing one.
Maintenance Page Definitions
Upgrade
Firmware | |
Upgrade via Manually Upload | |
Complete Upgrade | If enabled, all files will be replaced except user data. Default setting is disabled. |
Upload Firmware File to Update | Allows users to load the local firmware to the device to update the firmware. |
Upgrade via Network | |
Firmware Upgrade Mode | Allows users to choose the firmware upgrade method: TFTP, HTTP, HTTPS or Manual Upload. The default setting is “HTTP”. |
Firmware Server Path | Sets IP address or domain name of firmware server. The URL of the server that hosts the firmware release. Default is “fm.grandstream.com/gs”. |
HTTP/HTTPS Username | Enters the username for the firmware HTTP/HTTPS server. |
HTTP/HTTPS Password | Enters the password for the firmware HTTP/HTTPS server. |
Firmware File Prefix | Checks if firmware file is with matching prefix before downloading it. This field enables user to store different versions of firmware files in one directory on the firmware server. |
Firmware File Postfix | Checks if firmware file is with matching postfix before downloading it. This field enables user to store different versions of firmware files in one directory on the firmware server. |
Firmware Upgrade | Click the “Detect” button to check whether the firmware in the firmware server has an updated version, if so, update immediately. |
Config File | |
Use Grandstream GAPS | It is used to configure the download path and update mode for the configuration file server.
|
Config Upgrade Via | Selects provisioning method: TFTP, HTTP or HTTPS. Default setting is “HTTPS”. |
Config Server Path | Sets IP address or domain name of configuration server. The server hosts a copy of the configuration file to be installed on the device. Default is “fm.grandstream.com/gs”. |
HTTP/HTTPS Username | Configures the username for the config HTTP/HTTPS server. |
HTTP/HTTPS Password | Configures the password for the config HTTP/HTTPS server. |
Always send HTTP Basic Authentication Information | Includes configured username and password in HTTP request before receiving authentication challenge from the server. Default is “No”. |
Config File Prefix | Checks if configuration files are with matching prefix before downloading them. This field enables user to store different configuration files in one directory on the provisioning server. |
Config File Postfix | Checks if configuration files are with matching postfix before downloading them. This field enables user to store different configuration files in one directory on the provisioning server. |
Authenticate Conf File | Sets the device to authenticate configuration file before applying it. When set to “Yes”, the configuration file must include value P1 with phone system’s administration password. If it is missed or does not match the password, the device will not apply it. Default setting is “No”. |
XML Config File Password | Decrypts XML configuration file when encrypted. The password used for encrypting the XML configuration file is using OpenSSL. |
Download Device Configuration | Downloads the device’s configuration file in text format. The config file includes all the P value parameters for phone’s current settings except password for security purpose. Users can use the Grandstream configuration file generator to generate binary config file from this text file. |
Upload Device Configuration | Uploads configuration file to the device. Note: The GSC35XX supports the following config file format:
|
Provision | |
Automatic Upgrade | |
Automatic Upgrade | Specifies when the firmware upgrade process will be initiated; there are 4 options:
Note: Day of week is starting from Sunday. The default setting is “No”. |
Starting – Ending Hour of the Day (0 – 23) | Sets the time or time period of automatic upgrade, and automatically update during the set time or time period. |
Firmware Upgrade and Provisioning | Defines the device’s rules for automatic upgrade. It can be selected from:
The default setting is “Always Check at bootup”. |
DHCP Option | |
Allow DHCP option 43, option 160 and option 66 to Override Server | If DHCP option 43, 160 and 66 is enabled on the LAN side, the device will reset the CPE, upgrade, network VLAN tag, and priority configuration according to option 43 sent by the server. At the same time, the update mode and server path of the configuration upgrade mode will be reset according to the option 160 and 66 sent by the server. The default setting is “on”. The default setting is “Yes”. Notes: Reboot the device to make changes take effect. |
DHCP Option 120 Override SIP Server | Configures the device to allow the DHCP offer message to override the Config Server Path via the Option 120 header. The default setting is “Yes”. Note: Reboot to take effect. |
Allow DHCP Option 242 (Avaya IP Phones) | Enables DHCP Option 242. Once enabled, the device will use the configuration info issued by the local DHCP in Option 242 to configure proxy, transport protocol and server path. The default setting is “Yes”. Note: Reboot the device to make changes take effect. |
Config Provision | |
Download and Process All Available Config Files | By default, the device will provision the first available config in the order of cfgMAC, cfgMAC.xml, cfgMODEL.xml, and cfg.xml (corresponding to device specific, model specific, and global configs). If set to “Yes”, the device will download and apply (override) all available configs in the order of cfgMAC, cfg.xml, cfgMODEL.xml, cfgMAC.xml. |
Config Provision | Device will download the configuration files and provision by the configured order. Use arrow buttons to add and order configuration files. |
PNP Feature | |
PnP(3CX) Auto Provision | Sets the device to broadcast the SIP SUBSCRIBE message during booting up to allow itself to be discovered and be configured by the SIP platform. The default setting is “Yes”. Note: Reboot to take effect. |
Advanced Settings | |
Disable SIP NOTIFY Authentication | Disables the SIP NOTIFY Authentication on the device. If set to “Yes”, the GSC3510/GSC3505 will not challenge NOTIFY with 401. The default setting is “No”. |
Validate Certification Chain | Configures whether to validate the server certificate when download the firmware/config file. If it is set to “Yes”, the device will download the firmware/config file only from the legitimate server. Default setting is “No”. |
Set to allow access to the AutoConfig service. If not checked, access to service.ipvideotalk.com will be disabled. The default value is “Enabled”. | |
mDNS Override Server | Sets the device to broadcast the Multicast DNS (mDNS) message during booting up to allow itself to be discovered and be configured by the SIP platform. If it is set to “User Type A’, the device will broadcast the MDNS message “A_grandstream-cfg.local”; if it is set to “Use Type SRV”, the MDNS message will be “SRV_grandstream-cfg.local”. The default setting is “Use Type A”. |
Factory Reset | Resets the device to the default factory setting mode. |
System Diagnosis
Syslog | |
Select the transport protocol over which log messages will be carried.
| |
Syslog Server | Configures the URI which the device will send the syslog messages to. The default setting is “log.ipvideotalk.com”. |
Syslog Level | Selects the level of logging for syslog. The default setting is “None”. There are 4 levels from the dropdown list: DEBUG, INFO, WARNING and ERROR. The following information will be included in the syslog packet:
Note: Changing syslog level does not require a reboot to take effect. |
Syslog Keyword Filter | Only send the syslog with keyword, multiple keywords are separated by comma. Example: set the filter keyword to “SIP” to filter SIP log. |
Logcat | |
Clear Log | Clears the log files saved in the device. |
Log Tag | Configures the filter to display the specified process log file. |
Log Priority | Selects the log priority to display. It can be selected from list below:
|
Get Log | Displays the log file on the web page. |
Debug | |
One-click Debugging | |
One-click Debugging | Capture the checked info in the debugging list, click “Start” to debug if including “Capture trace” item and click “Stop” to end, Click “Capture” in another situation. All retrieved files will be generated to a package, and the last package will be overwritten, while the trace file will stay remain. |
Debug Info Menu | Display a list of info items that can be debugged, currently supports system logs, info log, capture package, tombstones and ANR log. The captured data can be viewed in “Debug information list”. The default is all selected. |
Debug Info List | You can select the existing debugging info package or grab package. Click the “Delete” button on the right to delete the file. |
View Debug Info | You can select the existing debugging info package or grab package. Click the “Delete” button on the right to delete the file. |
Core Dump | |
Enable Core Dump Generation | Configures whether to generate and save the core dump file when the program crashes. The default setting is “No”. Note: Reboot the device to make changes take effect. |
Core Dump List | Selects the existing core dump file in the drop-down box. Users could delete the file by pressing on “Delete” button. |
View Core Dump | Press “List” button to view all existing core dump files. The files are listed in chronological order, users could click the file name to download the file to the local computer. |
Record | Click to start capturing audio data, click the “Stop” button to end. To capture the audio data of the device can help to locate audio issues. The default is not enabled. You can record up to 1 minute audio data. |
Recording List | Choose the existing audio file. Click the “Delete” button on the right to delete this file. |
View Recording | Click on the “List” button to view. The captured audio data will be sorted by time. Click to download the data to the computer for analysis. |
Traceroute | |
Target Host | The IP address or URL for the Target Host of the Traceroute. Press Start to send traceroute request to configured target host. Press Stop to end traceroute running process. |
Ping | |
Target Host | The IP address or URL for the Target Host of the Ping. Press Start to send traceroute request to configured target host. Press Stop to end traceroute running process. |
NSLookup | |
Hostname | Enter a host name and find out the corresponding IP address. It will also do reverse name lookup and find the host name for an IP address you specify. |
Event Notification
Set the URL for events on phone web GUI, and when the corresponding event occurs on the device, the device will send the configured URL to SIP server. The dynamic variables in the URL will be replaced by the actual values of the device before sending to SIP server, in order to achieve the purpose of events notification. Here are the standards:
- The IP address of the SIP server needs to be added at the beginning and separate the dynamic variables with a “/”.
- The dynamic variables need to have a “$” at the beginning. For example: local=$local
- If users need to add multiple dynamic variables in the same event, users could use “&” to connect with different dynamic variables. For example: 192.168.40.207/mac=$mac&local=$local
- When the corresponding event occurs on the device, the device will send the MAC address and phone number to server address 192.168.40.207.
On Boot Completed | Configures the event URL when phone boots up. |
Incoming Call | Configures the event URL when phone has an incoming call. |
Outgoing Call | Configures the event URL when phone has an outgoing call. (Available for GSC3510 only) |
Missed Call | Configures the event URL when the device has new a missed call. |
On Connected | Configures the event URL when a call is established. |
On Disconnected | Configures the event URL when a call is disconnected. |
Forward On | Configures the event URL when the forward feature is enabled on the device. |
Forward Off | Configures the event URL when the forward feature is disabled on the device. |
On Blind Transfer | Configures the event URL when users transfer a call with blind transfer on the device. |
On Attended Transfer | Configures the event URL when users transfer a call with attended transfer on the device. |
Log On | Configures the event URL when users log on the device successfully. |
Log Off | Configures the event URL when users log off the device. |
On Register | Configures the event URL when an account in the device is registered successfully. |
On Unregister | Configures the event URL when an account in the device is unregistered. |
Application Page Definitions
Recording
File name | Displays the name of the recording file. |
Duration | Displays the duration of the device call. |
Date | Displays the date the call was recorded on. |
Operation | Delete, Modify, lock or download the recording file. Notes:
|
Music
Playback | |
Audio File | Please select the audio file type:
|
RTSP stream address | Supports RTSP stream address to obtain audio Ex : (rtsp://[IP]:[port]/[audio file name]), supporting MP3 and TS formats. |
Local Music | Displays the audio tracks uploaded to the cloud. It Supports .mp3 and .ogg audio formats only. |
Share Music | Prompts a popup browser tab or window from which the music will be streamed, play music on PC first, and click to select the music window to be shared to the GSC. It is recommended to use the browser Chrome (72 and above), Edge (79 and above), Otherwise it may be silent after sharing. |
Timed playback Click on "Add rule" to create Timed playback rule | |
Timed playback rule | |
Audio File | Please select the audio file type |
RTSP stream address / Local Music | If RTSP stream is selected: Support RTSP stream address to obtain audio(rtsp://[IP]:[port]/[audio file name]), supporting MP3 and TS formats. If Local Music is selected: Please select local music, supporting MP3 and OGG formats. |
Play Mode |
|
Play interval (s) | Configure the interval between the two playbacks. the valid range is 0-1800 seconds. |
Time | Set the trigger time, up to 3 items can be set. Click on "+" to add more |
Frequency | Configures the activation frequency from Monday to Sunday. Up to 7 days can be selected. Default value is not selected. |
Playback cascade
Playback Cascade | |
Cascade role Select the cascade role. Only cascading on the same network segment is supported and only one Master is allowed. You can set the cascade role to either "Slave", "Master", or "None", By Default, it is set to "Slave". | |
Multicast Address | In the case of a Master Cascade role, Enter the multicast address and port. As the Master, multicast will be initiated by this address. As the Slave, it will automatically obtain the address initiated by the Master. |
Forwarding Category | This options selects the type of audio to forward. it can be Music Media , call or alarm. |
Trigger Time Gives the option to add a triggering time for the Playback | |
Playback time | Configures the activation time. Up to 3 entries can be configured. When the activation time is not set, the default time is a full day. |
Frequency | Configures the activation frequency from Monday to Sunday. Up to 7 days can be selected. The default value is not selected. |
GSC Assistant
GSC Assistant | |
Managed by GSC Assistant App | Configures the ability for the device to be detectable by the GSC Assistant App. |
Device Label | Defines under what label the GSC shows up during the scan. |
Device Detection Page Definitions
Audio Loop Test
Available for the GSC3510 only
Audio loop test is used to test the three MICs available on the GSC3510. Each one of the MICs is tested separately.
Built-in Speaker Test
Built-in Speaker Test is used to test the GSC3510/GSC3505 by playing a piece of music in order to verify the sound quality.
LED Test
Led Test is used to test the availability of the four colored LEDs and their intensity. The colors of LEDs available on the GSC3510/GSC3505 are: Green, Red, Blue and White.
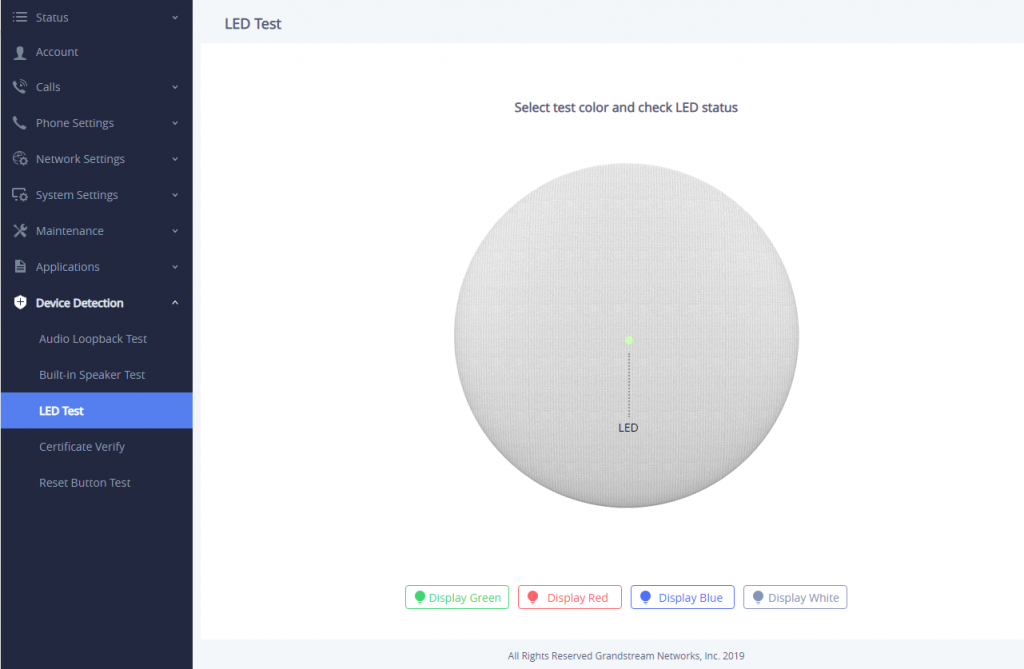
Certificate Verify
Certificate Verify is used to test the validity of the existing certificate.
Reset Button Test
Reset Button Test is used to test the Reset button, during the test the reset button doesn’t trigger factory reset, this feature allows the user to check if the button is responding.
Factory Reset
Restore to Factory Default via Web GUI
To perform factory reset to the GSC35XX via the Web GUI, please refer to following steps:
- Access to GSC35XX Web GUI using the using the default password.
- Navigate to Maintenance > Upgrade > Advanced Settings.
- Press Reset button and you may keep the network configuration by enabling Keep Network Configure as displayed on the following screenshots.
EXPERIENCING THE GSC3510/GSC3505
Please visit our website: https://www.grandstream.com to receive the most up- to-date updates on firmware releases, additional features, FAQs, documentation and news on new products.
We encourage you to browse our product related documentation, FAQs and User and Developer Forum for answers to your general questions. If you have purchased our products through a Grandstream Certified Partner or Reseller, please contact them directly for immediate support.
Our technical support staff is trained and ready to answer all of your questions. Contact a technical support member or submit a trouble ticket online to receive in-depth support.
Thank you again for purchasing Grandstream SIP Speaker, it will be sure to bring convenience and color to both your business and personal life.
CHANGE LOG
This section documents significant changes from previous versions of the user manual for the GSC35XX Series. Only major new features or major document updates are listed here. Minor updates for corrections or editing are not documented here.
Firmware Version 1.0.3.12
- Added ability to enable/disable “User” web access. [Enable User Web Access]
- Disabled the “User” Web UI account by default. [Enable User Web Access]
- Added a prompt to change password when logging in to account “User” for the first time. [New User Password]
Firmware Version 1.0.3.11
- Added support for RTP timeout. [RTP Timeout]
- Added option to Enable Weak TLS Cipher Suites. [TLS Cipher Suites]
- Added support for playing RTSP streams of IPv6 addresses. [RTSP stream address]
- Added the ability to change the web login timeout value. [User Login Timeout]
Firmware Version 1.0.3.8
- Added support for IPv6 over Wi-Fi. [WI-FI Support]
- Added ability to allow auto-answer by call-info/alert-info. [AUTO ANSWER BY CALL-INFO/ALERT-INFO]
- Increased limit of number of local music uploads to 50 files and increased single file size limit to 50 MB. [Local Music]
- Added support for GSC Assistant. [GSC ASSISTANT]
- Added ability to configure a time interval to periodically initiate a playback request to the RTSP server for music streaming. [Timed playback]
- Added ability to upload your own music files to be played for music streaming. [Local music]
- Added ability to schedule when to stream music. [Timed playback]
- Added support for receiving PTT multicasting. [Multicast/Group Paging]
- Added playback cascade feature. [Playback cascade]
- Added ability to provide the device MAC in the Hostname(Option 12) by using “$MAC”. [Hostname (Option 12)]
- Added the ability to resume a lower-priority multicast once a higher-priority multicast has ended. [Paging Priority Active]
- No major changes.
- Added support for Multicast Paging. [Paging]
- Added configurable option to specify the DNS cache duration. [DNS Failure Cache Duration]
- Added configurable option to specify the refresh timer for DNS queries. [DNS Refresh Timer]
- Added ability to hang up calls using the Sensor key. [Hang up]
- Added support for provisioning CA/User certificate from a remote server. [Wi-Fi Settings ]
- Added ability to configure Bluetooth device name. [Device Name]
- Added support for keeping the network configuration through a factory reset. [Factory Reset]
- No major changes.
- No major changes.
- Added ability to generate a zip file for multiple recording files. [Record]
- Added the missed calls notification on Web UI. [Missed Call Notification]
- Optimized web UI tooltips.
- Optimized the sensor functions of the device.
- Added the incoming rules options for each account [Incoming Call Rules]
- Added to support failover mechanism based on DNS SRV. [Register Before DNS SRV Fail-over]
- Added the ability to delay the auto-answer. [Automatic Answer Ringing Time (s]
- Added the ability to adjust the Busy Tone Expiration. [Busy Tone Ring Time (s)]
- Added support for visibility timeout to nearby devices. [Bluetooth]
- Added the option to Enable/Disable web access. [Security Settings]
- Added Ability to disable IP2location and Wifi Certification. [Allow AutoConfig service access]
- Added the ability to play/stream the music based on set schedule. [Music]
- Added the ability to support MP3 Format files on the Music Feature. [Music]
- Added the ability to display date/time on the Web UI. [System Info]
- Added the ability to stream Radio/Music on the device. [MUSIC/RADIO STREAMING]
- Added pairing PIN code with Bluetooth device. [BLUETOOTH PIN CODE]
- Added minimum & maximum TLS version. [MIN/MAX TLS VERSION]
- Added a prompt to restart the device after modifying PNP (3CX) Auto Provision
- Added an ability to adjust the volume during playing the radio/music
- Changed “DATE” for the time display under call history and recording files to “TIME AND DATE”
- Optimized web UI prompts
- Optimized the audio quality
- Added support for Date/Time settings. [Time Settings]
- Added volume control settings. [Preferences]
- Added support for Sensor Profile Schedule/ Profile Action. [2-pin Multi-Purpose Input Applications] [Sensor Settings]
- Added support for numbers with + on the whitelist/blacklist. [Black/White List Settings]
- Removed Red LED on missed call/voicemail when GSC3510 connected via Bluetooth. [GSC3510/GSC3505 LED Indicators]
- Removed Subscribe for MWI settings. [SIP Settings]
- Removed Voicemail Access Number settings. [General Settings]
- Removed SIP Display Name settings. [General Settings]
- This is the initial version.
